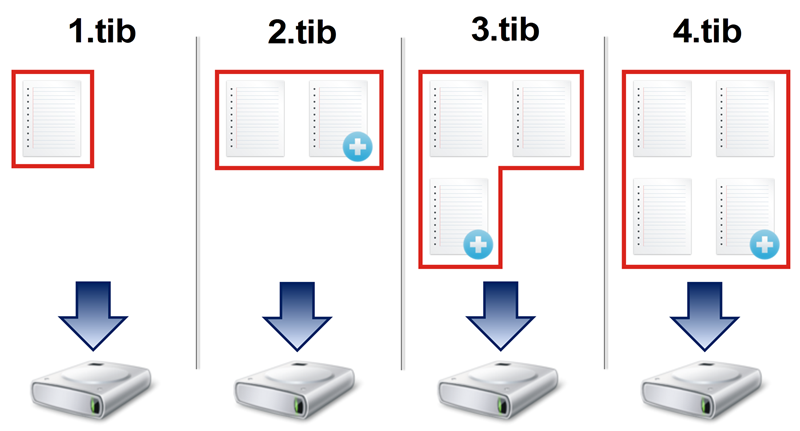
Acronis True Image 2018 offers three backup methods: full, incremental, and differential.
Full method
The result of a full method backup operation (also known as full backup version) contains all of the data at the moment of the backup creation.
Example: Every day, you write one page of your document and back it up using the full method. Acronis True Image saves the entire document every time you run backup.
1.tib, 2.tib, 3.tib, 4.tib—files of full backup versions.

Additional information
A full backup version forms a base for further incremental or differential backups. It can also be used as a standalone backup. A standalone full backup might be an optimal solution if you often roll back the system to its initial state or if you do not like to manage multiple backup versions.
Recovery: In the example above, to recover the entire work from the 4.tib file, you need to have only one backup version—4.tib.
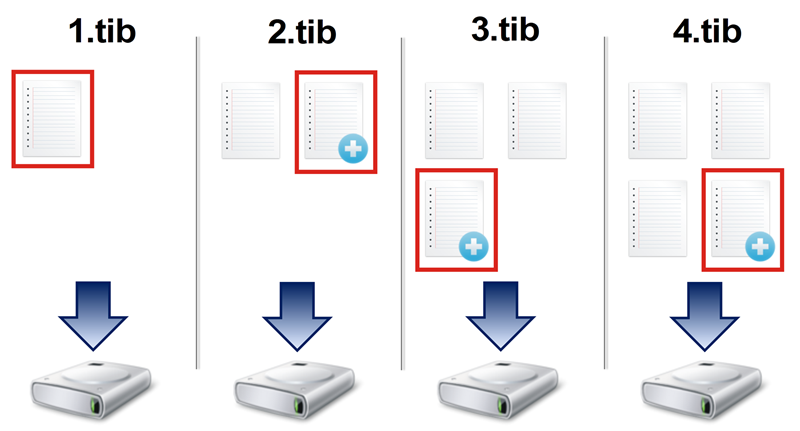
Incremental method
The result of an incremental method backup operation (also known as incremental backup version) contains only those files which have been changed since the LAST BACKUP.
Example: Every day, you write one page of your document and back it up using the incremental method. Acronis True Image saves the new page every time you run backup.
Note: The first backup version you create always uses full method.
Additional information
Incremental method is the most useful when you need frequent backup versions and the ability to roll back to a specific point in time. As a rule, incremental backup versions are considerably smaller than full or differential versions. On the other hand, incremental versions require more work for the program to provide recovery.
Recovery: In the example above, to recover the entire work from the 4.tib file, you need to have all the backup versions—1.tib, 2.tib, 3.tib, and 4.tib. Therefore, if you lose an incremental backup version or it becomes corrupted, all later incremental versions are unusable.
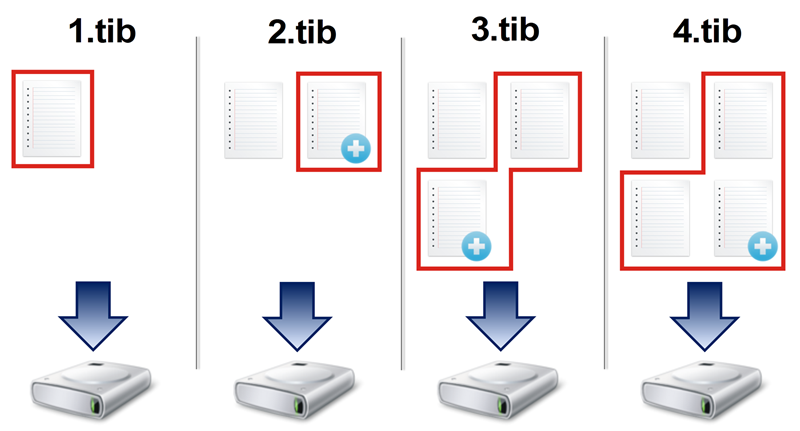
Differential method
The result of a differential method backup operation (also known as differential backup version) contains only those files which have been changed since the LAST FULL BACKUP.
Example: Every day, you write one page of your document and back it up using the differential method. Acronis True Image saves the entire document except the first page stored in the full backup version.
Note: The first backup version you create always uses full method.
Additional information
Differential method is an intermediate between the first two approaches. It takes less time and space than "Full", but more than "Incremental". To recover data from a differential backup version, Acronis True Image needs only the differential version and the last full version. Therefore, recovery from a differential version is simpler and more reliable than recovery from an incremental one.
Recovery: In the example above, to recover the entire work from the 4.tib file, you need to have two backup versions—1.tib and 4.tib.
To choose a desired backup method, you usually need to configure a custom backup scheme. For more information see Custom schemes.
An incremental or differential backup created after a disk is defragmented might be considerably larger than usual. This is because the defragmentation program changes file locations on the disk and the backups reflect these changes. Therefore, it is recommended that you re-create a full backup after disk defragmentation.
Changed Block Tracker (CBT)
The CBT technology accelerates the backup process when creating local incremental or differential disk-level backup versions. Changes to the disk content are continuously tracked at the block level. When a backup starts, the changes can be immediately saved to the backup.