When creating a backup plan, you specify the primary location for the backups. In addition, you can do the following:
Similarly, you can copy or move backups from a second location to a third location and so on. Up to five consecutive locations are supported (including the primary one).
Note: The replication feature replaces and enhances the Dual destination option, which was available in Acronis Backup & Recovery 10.
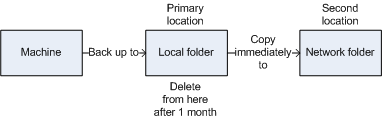
Example. You back up your machine to a local folder. The backup is immediately copied to a network folder. In the original local folder, the backup is stored for just one month.
The following picture illustrates this example.

Usage scenarios
Store your backups both on-site (for immediate recovery) and off-site (to secure the backups from local storage failure or a natural disaster).
Delete older backups from a fast storage according to retention rules, in order to not overuse expensive storage space.
Replicate the archive to the cloud storage by transferring only the data changes outside working hours.
Store your backups on a fast storage for as long as a need to access them is likely. Then, move them to a lower-cost storage to keep them there for a longer term. This enables you to meet legal requirements on data retention.
Back up overnight to a managed vault on a fast storage, and then let Acronis Backup Storage Node move the backups to tapes during the day.
Replication and retention in backup schemes
The following table shows availability of replication and retention rules in various backup schemes.
Backup scheme |
Can copy backups |
Can move backups |
Can delete backups |
Yes |
No |
No |
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Yes |
No |
Yes |
|
Yes |
No |
Yes |
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
No |
No |
No |
Notes: