Information store
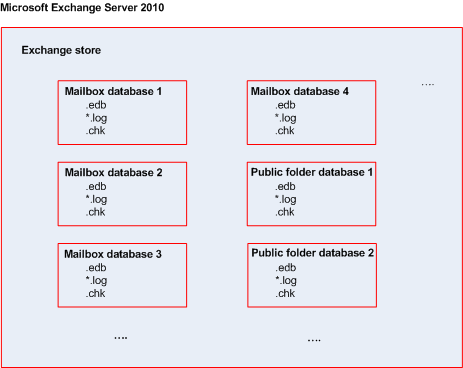
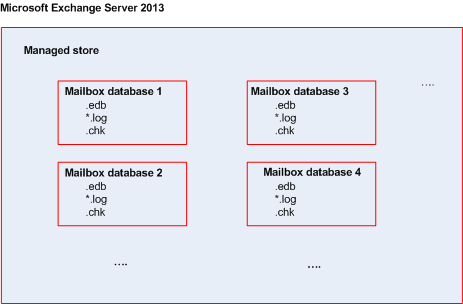
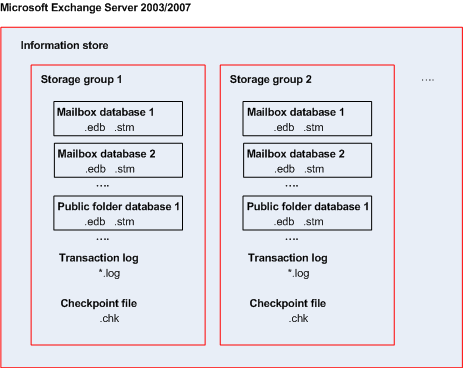
Microsoft Exchange Server stores its data in a single repository called information store (in Exchange 2003/2007), Exchange store (in Exchange 2010), or Managed store (in Exchange 2013). The primary components of the information store are storage groups (for Exchange 2003/2007 only) and Exchange databases.
Exchange database
There are two types of Exchange databases.
Either type database stores the data in the following files:
Contains message headers, message text, and standard attachments.
An Exchange 2003/2007 database uses two files: .edb for text data and .stm for MIME data.
Contains the history of changes made to the database. Only after a change has been securely logged, it is then written to the database file. This approach guarantees a reliable recovery of the database in a consistent state in case of a sudden database interruption.
Each log file is 1024 KB in size. When an active log file is full, Exchange closes it and creates a new log file.
Tracks how far Exchange has progressed in writing logged information to the database file.
Storage group
In Exchange 2003/2007, a storage group is a logical container for Exchange databases, the associated transaction log, checkpoint, and other system files. All databases in a storage group share a single log stream. A storage group is the basic unit for backup and recovery.
Starting with Exchange 2010, the concept of a storage group is discontinued. Therefore, you can select individual databases for backup. Each database will be backed up along with the necessary associated files.
Information store structure diagram
The following diagram illustrates the information store structure for Exchange 2003/2007, Exchange 2010, and Exchange 2013. The data items that you can back up at the database level are red-framed.