Data security is the term used to describe the process, policies, and technology that ensure a business’ data is secure and protected from unauthorized internal and external access or data corruption, including malicious attacks and insider threats. Before the days of digitization, a business could address data security by keeping the front door locked, sensitive paper files locked up in filing cabinets, and computers password protected. But with digital transformation, it now takes more effort and the latest technologies and tools to secure your systems, applications, and data.
Why should you consider data security?
Protect Your Intellectual Property
Your organization holds extremely sensitive business data that differentiates your company, products, and services. These include financial, customer, and R&D information, brand secrets, trade secrets, patents, formulas, recipes, designs, software code, search algorithms, and so on. All this data must be secure and protected as if it is leaked or lost, it can impact your company’s success and competitive position in your marketplace.
Ensure Compliance with Regulatory Requirements
Your business maintains a wealth of information about your customers and prospects. For example, if you are a B-to-C business, much of the consumer data you hold is private, whether it be Personally Identifiable Information (PII), PCI (card information), and Protected Health Information (PHI) – and must be secure from prying eyes.
If your business is subject to regulatory requirements, such as the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), and Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), compliance fines and investigative/remediation costs can be significant if you experience a data breach or leak.
Protect your Brand
In addition to compliance fines and remediation costs, a data leak can require you to compensate affected customers and/or in the worst case, customers may choose NOT to do business with you. This can impact your brand reputation and ultimately your future revenues.
Different data security technologies
There is an endless list of data security technologies that are used to protect systems, applications, and data. Here are but a few examples:
Data encryption is the process of encoding data in transit and at rest, typically using military grade AES-256 encryption. Next-generation anti-malware protection utilizes a multi-layered approach that incorporates artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML) and behavioral detection to catch both known and unknown threats. Vulnerability assessments are highly automated processes that search for known weaknesses in target systems — such as outdated software, unapplied patches, common gaps in network controls, or weaknesses in applications. URL filtering is a technology that blocks access to known malicious websites. It is mainly used to prevent users from reaching phishing websites that try to steal credentials, websites that operate as command-and-control servers (C&C), websites that download malware, and fake e-commerce shops that may steal money or cardholder data. Data loss prevention (DLP) is a technique that protects sensitive corporate data and personal data from leaving the company due to user negligence, mishandling of data, or malicious intent. DLP technologies enforce data use and handling policies by allowing or blocking data access and transfer operations based on a set of predefined security rules. Email security is a term that describes a multi-layered approach to protect email accounts and the information that’s part of email communications against unauthorized access, compromise, or data loss, including internal threats and malicious attacks. Bring your own device (BYOD) data security relates to a set of technologies that ensure employees’ personal devices used for business and the data they hold are secure from unauthorized access, corruption, or data loss. This includes protection against malware, ransomware, and cryptominers, capabilities to remotely wipe devices in case they are lost, and the ability to back up data on BYOD devices to ensure safe recovery. Patch management is the process of helping users identify, download, test, install, and verify patches, to ensure systems and applications stay up to date and secure. Patching can be a rigorous and time-consuming task for IT administrators, but automated solutions make it much easier. File sync and share solutions enable teams to collaborate, access company files, and share documents on any device, wherever they are, while IT maintains control over data security and compliance. Backup is the process of creating recoverable copies of data in case the original data is lost or compromised. Backup is a data protection technology and no business can consider their data and systems secure without regular backups. Disaster recovery (DR) is a strategic approach that uses backups to orchestrate failover and failback in the event of a disaster to minimize recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs). DR is a data protection technology and no business can consider their data and systems secure without a DR strategy.
What is the value of integrating different data security solutions?
To ensure your systems, applications, and data are secure and thoroughly protected, you will need to implement many of the technologies discussed above. However, in many cases, these technologies are offered as standalone point solutions. For example:
- Endpoint protection (EPP) does not include backup. DLP technologies are usually standalone or packaged with other compliance related technologies such as encryption.
- Email security is often provided as a standalone solution or add-on to an EPP solution.
- File sync and share is typically a standalone solution.
- Vulnerability assessments and patch management solutions are very often packaged as an add-on to an EPP or a Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) solution
But there is good news. Acronis offers a one-of-a-kind security solution that:
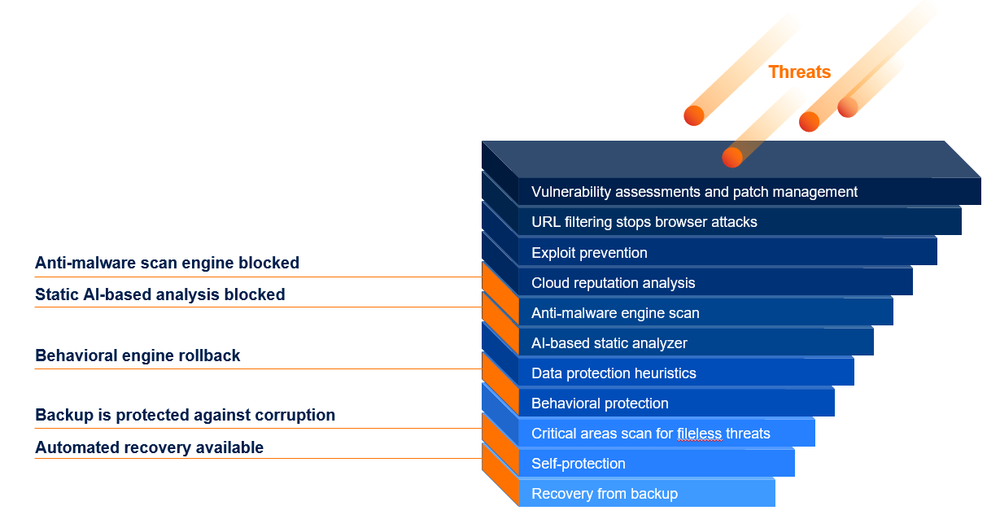
- Integrates security technologies to provide multiple layers of protection that help minimize the risk of malicious attacks, insider threats, and corrupted or deleted data due to human errors (See Figure 1.)
- Eliminates the inconsistencies, conflicts, and security gaps that point solutions can create when trying to work together
- Saves IT significant time and reduces manual errors
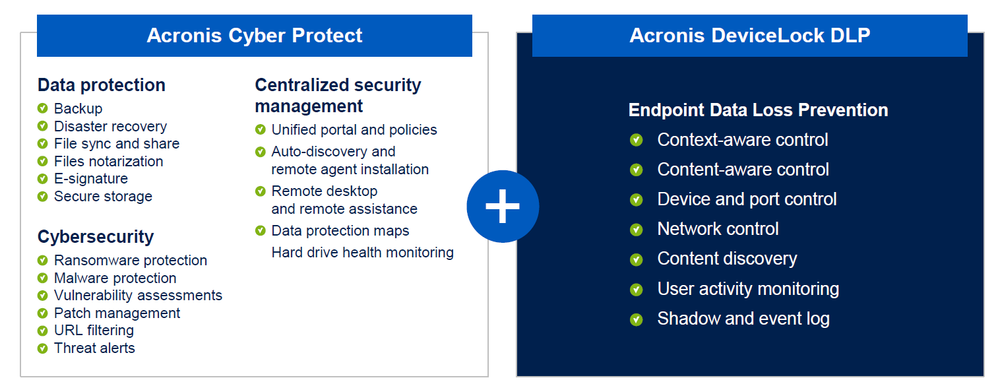
Acronis Cyber Protect – one solution for all things!
Acronis Cyber Protect is a one-of-a-kind solution that delivers complete cyber protection for modern threats, bringing together backup and data protection; next-generation, AI-based antimalware; and protection management into a single, integrated solution. It is unlike other security solutions that only bundle security tools and technologies or legacy, isolated point solutions for backup, anti-virus, patch-management, remote access, workload management, and monitoring and reporting tools.
Key features include:
Simplified administration with a single agent, single user interface, single platform Next-generation anti-malware with AI-based static and behavior detection combined with exploit prevention and URL filtering to counter known and unknown threats, including zero-day malware and ransomware Remote work protection to keep remote workers productive and protected with secure remote access to machines, remote wipe, prioritized patching, and protection against exploits for collaboration tools, etc. Vulnerability assessments and patch management functions to help you identify vulnerabilities before patching and prioritize patch management based on criticality Fail-safe patching to eliminate the risk of bad patches that render a system unusable. Before the latest patches are implemented, an image backup is automatically performed, enabling you to easily restore and roll back to a working state if there is an issue with a patch Protection for all key files with Acronis’ comprehensive Data Protection Map, which provides detailed information about stored data (classification, locations, protection status, and additional information) on your machines, detects whether the data is protected or not, and provides you with remediation options Real-time protection of important documents with Continuous Data Protection, which immediately saves all changes to critical files, even between backups, for near-zero RPOs Post-malware-attack recovery with integrated anti-malware scans and patch updates of backups Auto-response to emerging threats based on real-time alerts from Acronis Cyber Protection Operation Centers Forensic investigations based on digital evidence stored inside backups
If you are concerned about your ability to achieve enterprise data protection, Acronis Cyber Protect is the best choice when upgrading your outdated mess of backup, antivirus, and management and to get an easy, efficient, and secure solution that delivers upgraded security and productivity while decreasing operating costs.
Acronis also offers Acronis DeviceLock DLP, which provides comprehensive data loss prevention (DLP) for your business’ endpoints to minimize insider threats, gain visibility into data protection, and enforce process compliance. It can be combined with Acronis Cyber Protect to strengthen your security posture and prevent data leakage.
And there is more! Acronis offers a holistic approach to cyber protection with its top-tier cybersecurity services that focus on an organization’s people, processes, and technologies. Whether you are a small-to-medium-sized (SMB) business or enterprise, being prepared at every level – from infrastructure to application to personnel – greatly improves your organization’s cybersecurity posture.
About Acronis
Acronis is a Swiss company, founded in Singapore. Celebrating two decades of innovation, Acronis has more than 1,800 employees in 45 locations. The Acronis Cyber Protect Cloud solution is available in 26 languages in over 150 countries and is used by 20,000 service providers to protect over 750,000 businesses.