step 1: capturing billable activities
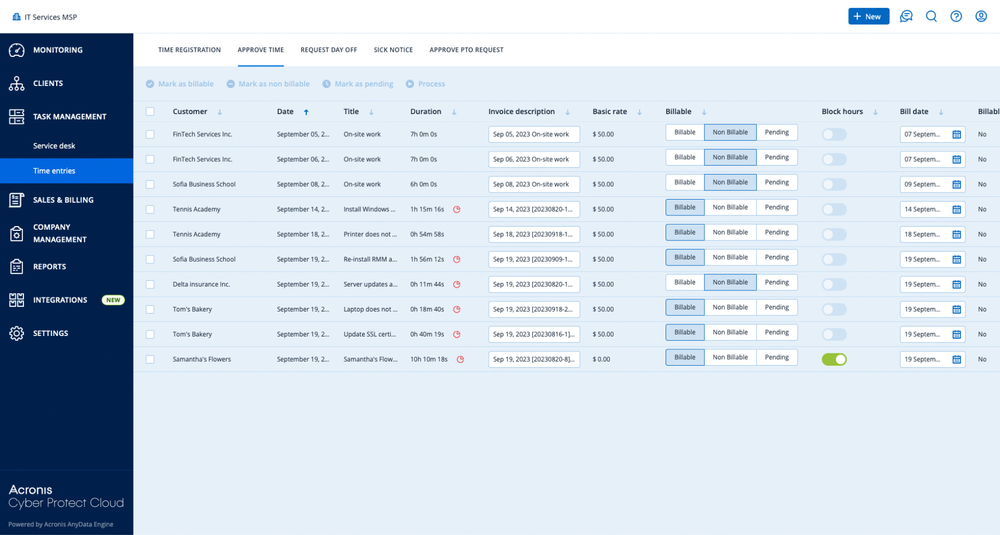
The automation journey starts with capturing billable activities across the MSP’s operations. A robust automated invoicing solution integrates directly with the MSP’s professional services automation (PSA) platform, where time entries, project milestones, and service tickets are logged.
• Technician time – Every minute spent on client tickets or project tasks is tracked and categorized as billable or non-billable.
• Recurring services – Managed services, SaaS licenses, and subscription-based offerings are automatically scheduled for monthly or annual billing.
• Cloud usage – Consumption data from cloud services (e.g., storage, backup, or cybersecurity) is collected and mapped to billing rules.
This ensures that no billable item is overlooked, closing one of the most common revenue leaks in MSP businesses.
step 2: applying billing rules and pricing models
Once activities are captured, billing automation software applies predefined rules that reflect the MSP’s pricing structure. This step eliminates guesswork and ensures consistency.
• Hourly rates and role-based pricing – The system automatically applies the right rate for each technician or service role.
• Recurring subscriptions – Contracts are billed automatically at the agreed frequency without manual intervention.
• Usage-based billing – Cloud consumption and per-device pricing are calculated against usage metrics.
• Discounts and custom rules – The system enforces pre-agreed discounts or client-specific billing conditions.
By standardizing how charges are applied, MSPs avoid underbilling and reduce disputes.
step 3: generating automated invoices
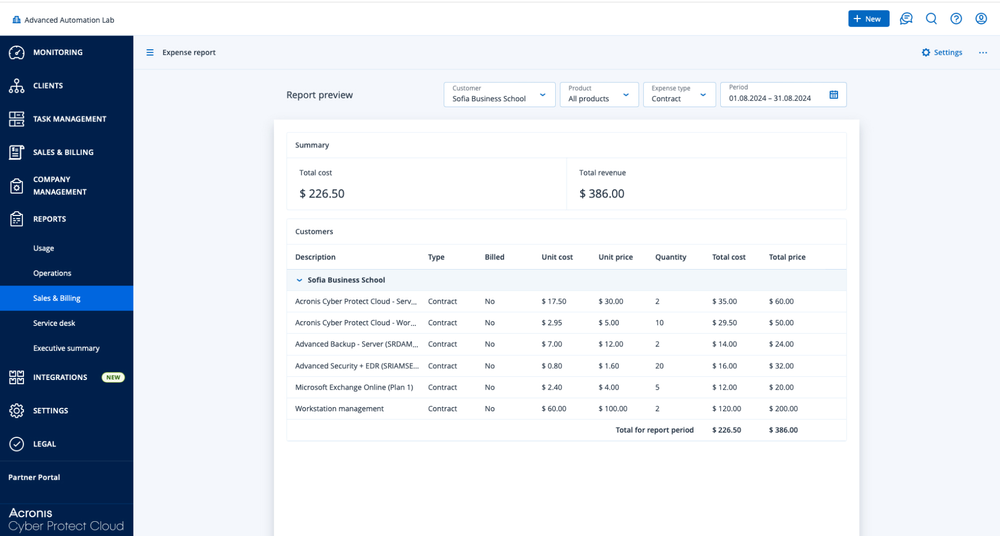
After billing rules are applied, the system generates invoices automatically. This process consolidates all activities into a single, accurate, and transparent invoice.
Each invoice includes:
• Itemized service lines (time, projects, cloud services, subscriptions)
• Rates and discounts clearly displayed
• Automated tax calculations where applicable
• Company branding and professional formatting
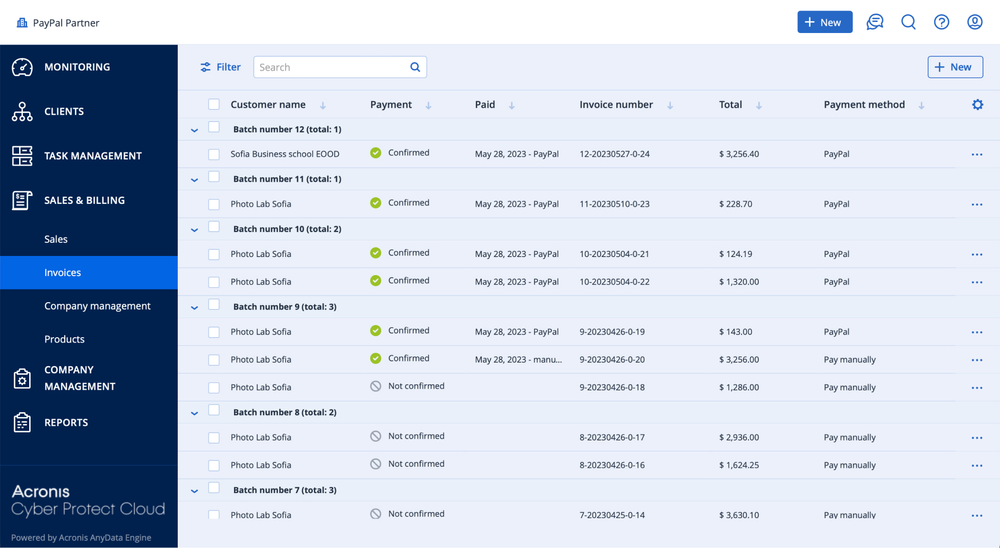
Invoices can be scheduled to generate at regular intervals (e.g., monthly) or triggered by specific events (e.g., project completion). For clients, this creates a predictable billing rhythm, improving trust and reducing disputes.
step 4: syncing with accounting systems
Billing automation doesn’t end at invoice creation. To close the financial loop, invoices are synced with accounting systems such as QuickBooks Online, Xero, FreshBooks, or Sage.
This integration ensures:
• No duplicate data entry
• Consistent records across PSA and accounting systems
• Simplified reconciliation at month-end close
• Faster financial reporting and visibility into accounts receivable
By eliminating the need for manual entry, finance teams save hours each billing cycle.
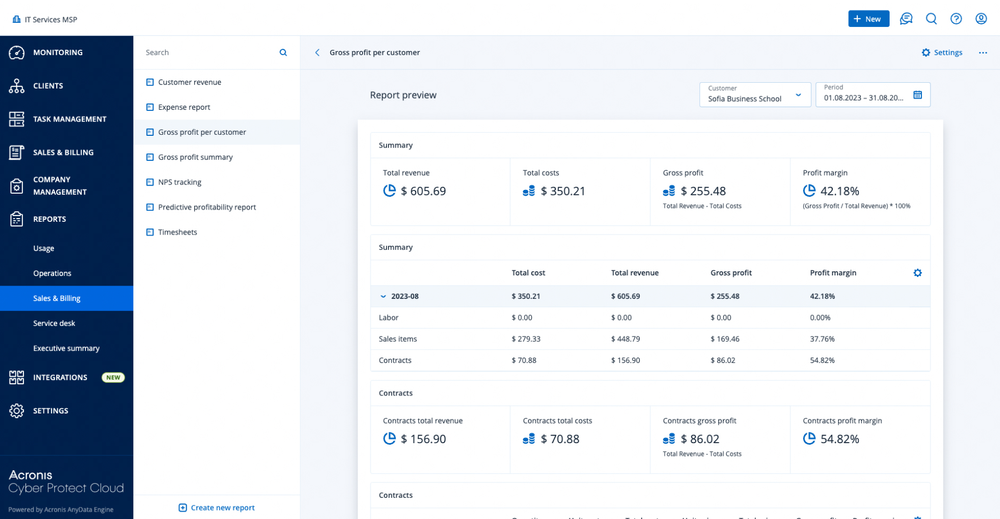
step 5: tracking performance and profitability
A major advantage of billing automation software for MSPs is the ability to generate reporting and analytics. Automated billing platforms typically include dashboards for:
• Revenue recognition – Track revenue by client, service type, or period.
• Profitability insights – Identify underperforming contracts or services.
• Outstanding invoices – Monitor unpaid invoices to reduce DSO.
• Technician utilization – See how time is spent and whether billable targets are met.
These insights help MSPs refine their pricing models, optimize service offerings, and improve long-term profitability.