Creating custom algorithms
Algorithm definition
The Algorithm definition step shows you a template of the future algorithm.
The table has the following legend:
- The first column contains the type of operation (to write a symbol to disk; and to verify written).
- The second column contains the pattern of data to be written to disk.
Each line defines an operation that will be performed during a pass. To create your algorithm, add as many lines to the table that you think will be enough for secure data destruction.
To add a new pass
-
Click Add. The Wiping Pass Adjustment window opens.
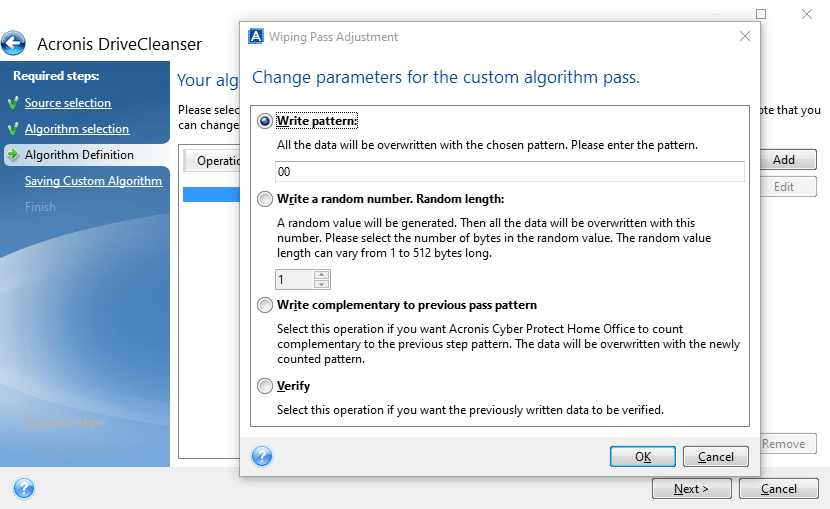
-
Choose an option:
-
Write pattern
Enter a hexadecimal value, for example, a value of this kind: 0x00, 0xAA, or 0xCD, etc. These values are 1 byte long, but they may be up to 512 bytes long. Except for such values, you may enter a random hexadecimal value of any length (up to 512 bytes).
If the binary value is represented by the 10001010 (0x8A) sequence, then the complementary binary value will be represented by the 01110101 (0x75) sequence.
-
Write a random number
Specify the length of the random value in bytes.
-
Write complementary to previous pass pattern
Acronis Cyber Protect Home Office adds a complementary value to the one written to disk during the previous pass.
-
Verify
Acronis Cyber Protect Home Office verifies the values written to disk during the previous pass.
-
- Click OK.
To edit an existing pass
-
Select the corresponding line, and then click Edit.
The Wiping Pass Adjustment window opens.
When you select several lines, the new settings will be applied to all of the selected passes.
- Change the settings, and then click OK.
Saving algorithm to a file
- On the Saving custom algorithm step, select Save to a file, and then click Next.
- In the window that opens, specify the file name and location, and then click OK.