Site-to-site Open VPN connection
To understand how networking works in Disaster Recovery, we will consider a case when you have three networks with one machine each in the local site. You are going to configure the protection from a disaster for the two networks – Network 10 and Network 20.
On the diagram below, you can see the local site where your machines are hosted, and the cloud site where the cloud servers are launched in case of a disaster.
With Disaster Recovery, you can fail over all the workload from the corrupted machines in the local site to the cloud servers in the cloud.
You can add and manage up to 23 networks in the cloud.
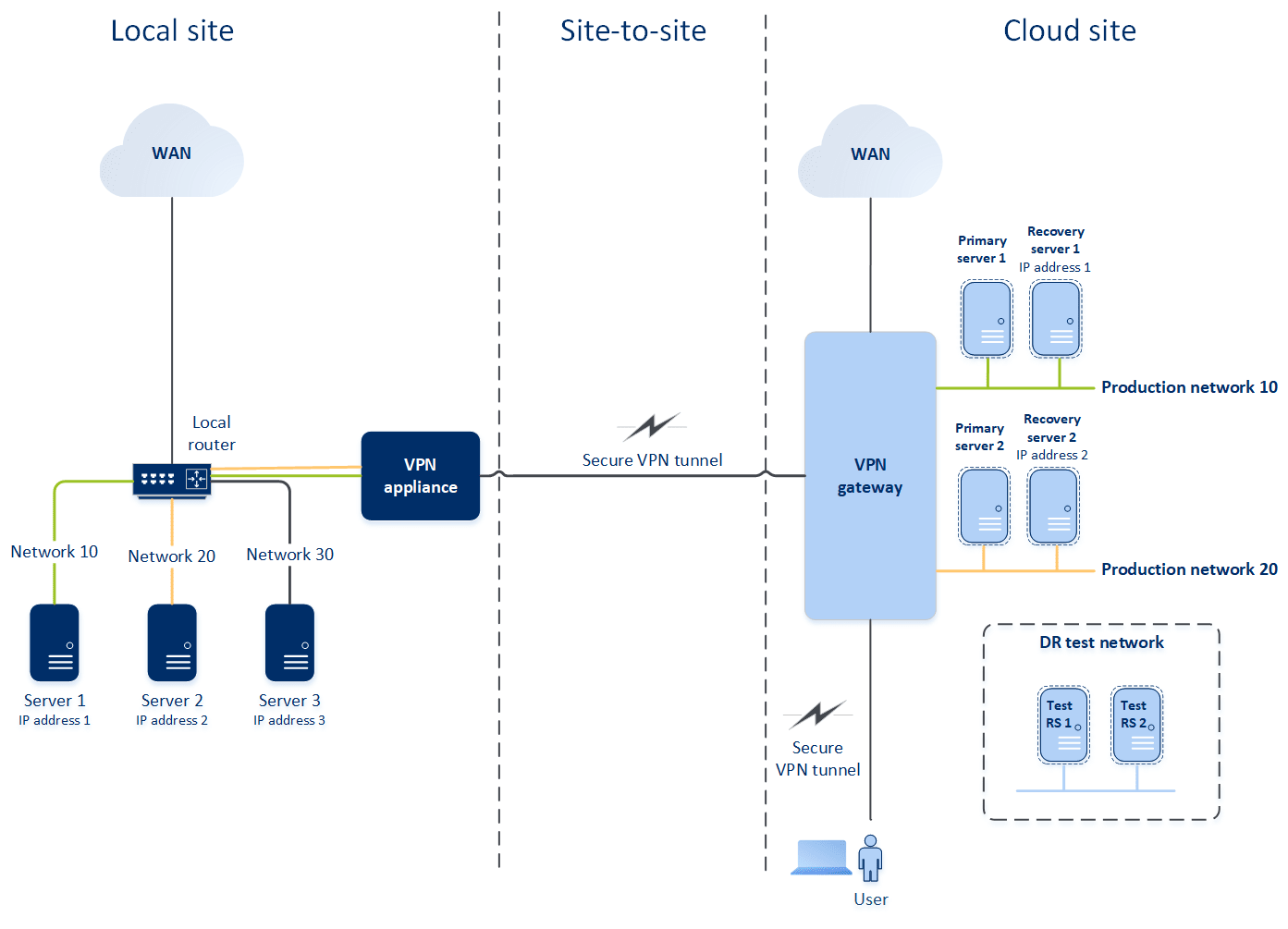
To establish a Site-to-site Open VPN connectivity between the local and cloud sites, a VPN appliance and a VPN gateway are used.
When you start configuring the Site-to-site Open VPN connectivity in the Cyber Protect console, the VPN gateway is automatically deployed in the cloud site.
After the VPN gateway is deployed, you must do the following:
- Deploy the VPN appliance on your local site.
- Add the networks that you want to be protected.
- Register the VPN appliance in the cloud.
Disaster Recovery will create a replica of your local network in the cloud. A secure VPN tunnel will be established between the VPN appliance and the VPN gateway. This VPN tunnel will provide your local network extension to the cloud. The production networks in the cloud will be bridged with your local networks. The local and cloud servers will communicate through this VPN tunnel as if they are all in the same Ethernet segment. Routing will be performed by your local router.
For each source machine that you want to protect, you must create a recovery server on the cloud site. It will stay in the Standby state until a failover event happens. If a disaster happens and you start a failover process (in the production mode), the recovery server representing the exact copy of your protected machine will be started in the cloud. It may be assigned the same IP address as the source machine, and it can be started in the same Ethernet segment. Your clients will continue working with the server, not noticing any background changes.
You can also start a failover process in the test mode. This means that the source machine will be working and, at the same time, the respective recovery server with the same IP address will be started in the cloud. To prevent IP address conflicts, a special virtual network will be created in the cloud – test network. The test network will be isolated to prevent duplication of the source machine IP address in one Ethernet segment. To access the recovery server in the test failover mode, when you create a recovery server, you must assign a Test IP address to it. There are other parameters for the recovery server that you can configure, too.
How routing works
When a Site-to-site connection is established, routing between cloud networks is performed by your local router. The VPN server does not perform routing between cloud servers located in different cloud networks. If a cloud server from one network wants to communicate with a server from another cloud network, the traffic goes through the VPN tunnel to the local router on the local site, then the local router routes it to another network, and it goes back through the tunnel to the destination server on the cloud site.
VPN gateway
The VPN gateway is the major component that enables communication between the local and cloud sites. It is a virtual machine in the cloud on which the special software is installed, and the network is specifically configured. The VPN gateway has the following functions:
- Connects the Ethernet segments of your local network and production network in the cloud in the L2 mode.
- Provides iptables and ebtables rules.
- Works as a default router and NAT for the machines in the test and production networks.
- Works as a DHCP server. All machines in the production and test networks get the network configuration (IP addresses, DNS settings) via DHCP. Every time a cloud server will get the same IP address from the DHCP server. If you need to set up the custom DNS configuration, you should contact the support team.
- Works as a caching DNS.
VPN gateway network configuration
The VPN gateway has several network interfaces:
- External interface, connected to the Internet
- Production interfaces, connected to the production networks
- Test interface, connected to the test network
In addition, two virtual interfaces are added for Point-to-site and Site-to-site connections.
When the VPN gateway is deployed and initialized, the bridges are created – one for the external interface, and one for the client and production interfaces. Though the client-production bridge and the test interface use the same IP addresses, the VPN gateway can route packages correctly by using a specific technique.
VPN appliance
The VPN appliance is a virtual machine on the local site with Linux that has special software installed, and a special network configuration. It enables the communication between the local and cloud sites.