Alerts Settings: SNMP
Use the SNMP tab in the Alerts Settings dialog box to configure DeviceLock Content Security Server for SNMP support.
To open this dialog box, do either of the following:
•Right-click Alerts in the console tree, and then click Manage.
•Select
Alerts in the console tree, and then click
Manage 
on the toolbar.
•Select Alerts in the console tree; then, in the details pane, right-click SNMP and click Manage.
•Select Alerts in the console tree, and then double-click SNMP in the details pane.
DeviceLock supports SNMPv1, SNMPv2c, and SNMPv3 protocols. You can configure DeviceLock Content Security Server to automatically send alert notifications to the specified SNMP server when alert conditions occur. These alerts are sent only when all of the following conditions are met:
•The SNMP server is set up to receive traps.
•The remote computer running the SNMP server is accessible from computers where the discovery task is being performed (by the Agent) or from the server (in case of agentless scanning).
•Alerts have been configured to be sent through SNMP traps.
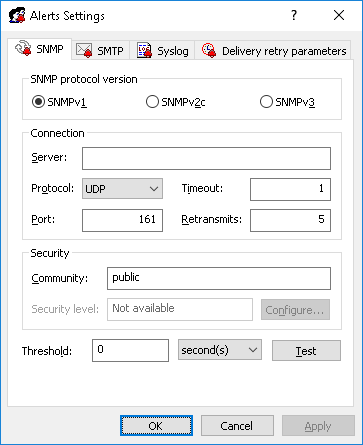
Complete the SNMP tab as follows:
•SNMP protocol version - Choose the SNMP protocol version required by your SNMP server. Available options are: SNMPv1, SNMPv2c, and SNMPv3.
•Connection - Supply the SNMP server-related information:
•Server - The SNMP sever to send traps to. In the Server box, type the SNMP server host name or IP address.
•Protocol - The transport protocol for passing data between DeviceLock and the SNMP server. Available options are: UDP and TCP.
•Timeout - The time (in seconds) that DeviceLock waits for the SNMP server to reply before retransmitting the data packet. The default value is 1 second.
•Port - The port on which the SNMP server listens for traps. The default port is 161.
•Retransmits - The number of times a request is re-sent to the SNMP server, if the server is not responding (applies only to the TCP protocol). The default value is 5.
•Security - Configure SNMP security settings:
•Community (if SNMPv1 or SNMPv2c is selected) - The SNMP community name to use for authentication with the SNMP server. The default value is public.
•User name (if SNMPv3 is selected) - The name of the user account to use for authentication with the SNMP server. To specify a user name, click the Configure button next to the Security level box. If authentication is not required, a user name may not be specified.
•Security level (if SNMPv3 is selected) - A value indicating the security level of SNMP communication. Possible values:
•No security - Communication using neither authentication nor encryption.
•Authentication - Communication using authentication without encryption.
•Authentication and Privacy - Communication using both authentication and encryption.
•Configure (if SNMPv3 is selected) - Click the Configure button next to the Security level box, to specify the following settings:
•Security user name - Supply the name of the user account to use for authentication with the SNMP server. If authentication is not required, this field can be left blank.
•Context name - Supply the context name, as required by SNMP server.
•Context engine ID - Supply the context engine ID, as required by SNMP server.
•Authentication protocol - Choose the protocol used to encrypt the authentication with the SNMP server. Available options:
•None - Security level of No security.
•HMAC-SHA - Security level of Authentication or Authentication and Privacy, depending upon the Privacy protocol setting.
•Password/ Confirm password - Supply the password of the user account to use for authentication with the SNMP server (applies to the Authentication protocol setting).
•Privacy protocol - Choose the protocol used to encrypt data for SNMP communication. Available options:
•None - Security level of No security or Authentication, depending upon the Authentication protocol setting.
•CBC-AES-128 - Security level of Authentication and Privacy, requires the Authentication protocol setting other than None.
•Password/ Confirm password - Supply the password for data encryption (applies to the Privacy protocol setting).
•Threshold - Specify the time interval (in hours, minutes or seconds) used for event consolidation when generating alerts. DeviceLock consolidates multiple similar events occurring within the threshold time and generates a summary in a single alert if all of the following conditions are true:
a) The events are of the same type, either Success for actions successfully performed on discovered content, or Failure for failed actions.
b) The Reason and Computer of the events being wrapped are the same.
The default value is 0 seconds.
•Test - Click to send a test SNMP trap to verify that DeviceLock is configured correctly. This test operation can have two different outcomes, each resulting in a different message being displayed:
•The test can complete successfully, meaning that a test SNMP trap was successfully sent using the configured SNMP trap parameters. The resulting message states: “Test SNMP alert was successfully sent.”
•The test can fail, meaning that a test SNMP trap was not sent. The resulting message states: “Test SNMP alert was not sent due to error: <error_description>.”
SNMP traps by DeviceLock Discovery are presented in the Management Information Base (MIB) format. MIB for DeviceLock Discovery has the object identifier (OID) 1.3.6.1.4.1.60000 or iso.org.dod.internet.private.enterprise.DeviceLock, and it contains the following branch nodes:
•products(1)
•discoveryAgent(1)
•alerts(1) - This node contains one instance of each of the following MIB objects:
•eventType(1) - The class of an event: either Success for allowed access or Failure for denied access. Note that the value of eventType is displayed as a numeric value raher than a text string: 8 indicates Success, 16 indicates Failure.
•computerName(2) - The name of the computer from which the event was received.
•action(3) - The user’s activity type.
•name(4) - The name of the discovered object.
•reason(5) - The cause of the event.
•datetime(6) - The date and time (in the RFC3339 date/time format) when the content discovery event has occurred.
A trap is sent just once each time an event associated with an alert occurs. Below is an example of the SNMP alert.

 on the toolbar.
on the toolbar.