DeviceLock Administrators
This parameter allows you to define the list of user accounts with administrative access rights to DeviceLock Service.
Click Properties on the shortcut menu of the DeviceLock Administrators item to open the configuration dialog box.
DeviceLock’s default security configuration is based on Windows Access Control Lists (ACL). A user without administrative privileges can’t connect to DeviceLock Service, modify its settings or remove it. Everything is controlled by the Windows security subsystem.
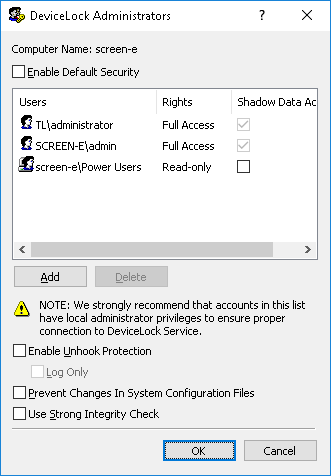
To turn on the Windows ACL-based security, select the Enable Default Security check box.
Note: As described in the
Basic Security Rules section of this manual, giving administrative privileges to regular users is strongly discouraged. |
Users with local administrator privileges (i.e. members of the local Administrators group) can connect to DeviceLock Service using a management console and change permissions, auditing and other parameters. Moreover, such users can uninstall DeviceLock from their computers, disable or delete DeviceLock Service, modify a service’s registry keys, delete a service’s executable file, and so on. In other words, users with local administrator privileges can circumvent the default security based on Windows ACL.
However, if for some reason, users in your network have administrator privileges on their local computers, DeviceLock does provide another level of protection - DeviceLock Security. When DeviceLock Security is enabled, no one except authorized users can connect to DeviceLock Service or stop and uninstall it. Even members of the local Administrators group (if they are not on the list of authorized DeviceLock administrators) can’t circumvent DeviceLock Security.
To turn on DeviceLock Security, clear the Enable Default Security check box.
Then you need to specify authorized accounts (users and/or groups) that can administer DeviceLock Service. To add a new user or user group to the list of accounts, click the Add button. You can add several accounts simultaneously.
To delete a record from the list of accounts, use the Delete button. Using Ctrl and/or Shift you can highlight and remove several records simultaneously.
To determine the actions allowed to a user or group, select the desired level of access:
•Full access - Allows the user or group to modify permissions, auditing and other parameters, remove and update DeviceLock Service.
•Change - Allows the user or group to change settings, install, and uninstall DeviceLock Service. Unlike full access, does not give the right to make changes to the list of DeviceLock administrators or change access rights for existing users or groups in that list.
•Read-only - Only allows the user or group to view permissions, auditing and other parameters. Users can view defined parameters but cannot modify anything or remove/update DeviceLock Service.
For users and groups with
Change or
Read-only access, the
Shadow Data Access option can be selected to allow access to shadow copies and user activity records. The users and groups with this option selected are allowed to open, view, and save shadow copies and user activity records from DeviceLock Service logs by using Shadow Log Viewer (see
Shadow Log Viewer (Service)) and UAM Log Viewer (see
Viewing User Activity).
Note: Without access to shadow data, DeviceLock Service administrators do not have access to the content of shadow copies and user activity records. They cannot open, view, or save shadow copies and records of user activity. |
We strongly recommend that DeviceLock Service administrators be given local administrator rights as installing, updating, and uninstalling DeviceLock Service may require access rights to Windows Service Control Manager (SCM) and shared network resources.
Consider the following recommendation to properly define the list of DeviceLock administrators: Add the Domain Admins group with Full access rights to this list. Since the Domain Admins group is a member of the Administrators local group on every computer in the domain, all members of Domain Admins will have full access to the DeviceLock Service on every computer. However, other members of the Administrators local group will not be able to administer the DeviceLock Service or disable it.
Select the Enable Unhook Protection check box to turn on protection against anti-rootkits that might be maliciously used to disable the DeviceLock Service. With this protection turned on, any attempt to violate the integrity of the DeviceLock code will cause a fatal error in Windows (BSOD).
Note: Some antivirus, firewall and other low-level third-party software may conflict with the unhook protection and cause fatal errors (BSOD). We recommend that you enable this protection only for the systems where it was tested before. |
If you select the Log Only check box, DeviceLock does not cause Windows to stop with a fatal error (BSOD) when a violation is found. Instead, the event about this violation is written into the audit log.
Select the Prevent Changes In System Configuration Files check box to instruct DeviceLock Service to automatically secure the Windows Hosts file.
Note: Because DeviceLock uses the local Hosts file for host name resolution, a malicious user with local administrator rights can modify the Hosts file as required to bypass DeviceLock security policies. In order to minimize security risks, we recommend that you secure the Hosts file using the Prevent Changes In System Configuration Files option. |
Also, by selecting or clearing the Use Strong Integrity Check check box, you can specify the type of integrity checks to use. You can run two types of integrity checks to detect corruption in DeviceLock Service’s executable files:
•Simple integrity check: DeviceLock Service checks version information of all its executable files. To specify this type of integrity checks, clear the Use Strong Integrity Check check box.
•Strong integrity check: DeviceLock Service verifies the digital signatures of all its executable files. To specify this type of integrity checks, select the Use Strong Integrity Check check box. A strong integrity check requires more time than a simple integrity check.
Recommendations
With default security disabled and a list of DeviceLock Administrators set up, access to network drives and physical ports on the client computer might be unexpectedly blocked regardless of the effective access permissions. A side effect is that Task Manager does not list the DeviceLock Service process (dlservice).
This behavior is part of the protection against administrators who have full access to the client computer but are not included in the list of DeviceLock administrators. If the DeviceLock Service unexpectedly stops, this protection feature blocks access to the channels of possible data leaks.
Restart the computer to restore DeviceLock access settings. If the problem reappears, try disabling the antivirus software that could force the DeviceLock Service to stop.