Recovery Point Objective (RPO)
Location: on the Dashboard page.
Access path: Dashboard tab on the menu bar.
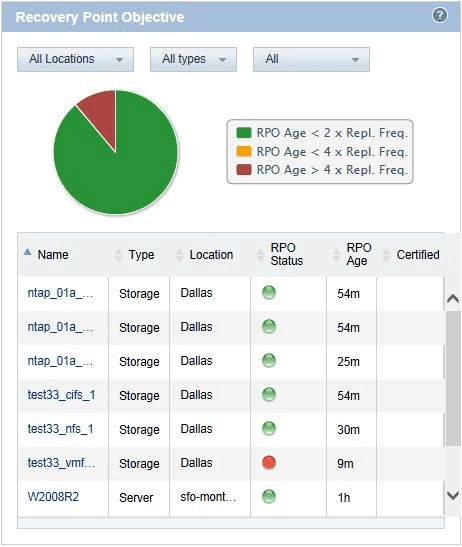
This pane presents the status of snapshot history relative to RPO for Local Recovery and Remote Recovery servers and for NetApp storages.
RPO is the maximum tolerable period of time in which data might be lost due to a major incident. In other words, RPO is the maximum tolerable interval between snapshots.
If you set the desired RPO value and select the Check RPO Health check box in the server or storage details, the Recovery Console compares the latest snapshot age with the set RPO value and shows the result on the Recovery Point Objective pane.
There are three possible RPO statuses, they are based on the age of the last snapshot:
- Green status: Servers and storages whose last snapshot is no older than twice the RPO interval.
- Yellow status: Servers and storages whose last snapshot is older than twice the RPO interval and no older than four times the RPO interval.
- Red status: Servers and storages whose last snapshot is older than four times the RPO interval.
If snapshots of a server or a storage are taken within a certain time interval (for example, during working hours), the RPO status outside of this interval is not changed.
If the RPO status for a "Local" location is RED, then the RPO status for the corresponding "Cloud" location (i.e., Dallas, Ashburn, etc.) will also be RED (or will be soon) as the local copy is the source of the cloud data.
You can follow up on servers with yellow or red status. If the server is local and contains snapshots taken by FalconStor:
- Verify that FalconStor DiskSafe on the server is functioning properly. Verify that all applicable services—FalconStor DiskSafe, Intelligent Management Agent, Microsoft iSCSI—are running.
- If DiskSafe is found to be functioning properly, check the available storage on the CDP where this server is protected (can be viewed under Admin, Reports, Acronis Local Cloud Hubs Storage Report).
- If CDP storage is the culprit, open a support ticket.
- If you cannot determine why the status is not green, open a support ticket.
If the server is local and contains snapshots taken by Acronis:
- Verify that the Acronis Managed Machine Service is running on the production server.
- Verify that the local Acronis Storage Node is functioning properly. To do so, use either Remote Desktop (RDP) or vSphere Client to check that the virtual machine with Acronis Storage Node is powered on and that the Acronis Storage Node Service is running.
- Check the network connection between the server and the storage node.
- Verify that the production server backups are successfully created on the local Acronis Storage Node. To do so, use RDP to connect to the machine with Acronis Backup Management Server. There, check the production server status, check the available space in the managed vault where the backups are stored, and access the vault to verify that the backups are present there.
- If you cannot determine why the status is not green, open a support ticket.
If the server is remote:
- Determine how many servers are RED.
- If only a few remote servers are RED, see solution for local servers.
- If all servers are GREEN locally but RED remotely, check VPN connectivity to the cloud.
- If VPN connectivity is established and operating correctly, open a support ticket.
- If VPN connectivity is found to be in error on the Acronis site, open a support ticket.
Available operations:
-
Filter the data by selecting one of the following:
- a different cloud location, local or remote, in the drop-down list box.
- a different object type in the drop-down list box.
- a different certification status in the drop-down list box.
- a colored (status) wedge in the pie chart.
- Drill-down to a server’s details by clicking its name in the server list.
- Open a tooltip showing the certification details for a particular server by holding the mouse pointer over its Certified icon.
See also: