By Iliyan Gerov, Product Marketing Manager, Acronis
What is personal data and why does it need protection? In today’s digital world, personal data is more valuable than ever. It includes any information that can be used to identify an individual, such as names, phone numbers, email addresses, financial details and even online behavior patterns. Such data is collected by businesses worldwide to perform their day-to-day operations.
However, with the rise of cyberthreats and data breaches, protecting personal data is crucial to prevent identity theft, financial fraud and unauthorized surveillance.
To answer the rising risks, governments worldwide are implementing stringent regulations to safeguard personal data. India’s Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023, is landmark legislation that aims to protect personal data and regulate its processing, including collection, storage, usage, sharing, disclosure, erasure, etc. This article will help you navigate the regulatory requirements of the DPDP Act and provide you with practical ways to protect personal data — to prevent it from ending in the wrong hands or to avoid regulatory penalties. Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act overview The DPDP Act, 2023 establishes clear rules for businesses and organizations that handle personal data. It defines the roles and responsibilities of different entities, ensures Data Principals (individuals) have control over their data, and mandates compliance measures for Data Fiduciaries (entities handling personal data). DPDP Act applicability The DPDP Act applies to:
- Digital personal data collected within India.
- Personal data of Data Principals within India, processed outside of India if it relates to offering goods or services in India.
Data Principal and Data Fiduciary There are two main entities when it comes to DPDP Act:
- Data Principal – The individual whose personal data is being processed.
- Data Fiduciary – Any entity (business, government or individual) that determines why and how personal data is processed. It’s also worth noting that any person who processes personal data on behalf of a Data Fiduciary is called “Data Processor.” Note: Government organizations can be exempt from the DPDP Act regulatory requirements.
Main rights and duties of Data Principals
The DPDP Act grants individuals several rights, including:
- Right to Information and Access — Individuals can request details on how their data is being processed.
- Right to Correction and Erasure — Individuals can request corrections or deletion of their data.
- Right of Grievance Redressal — Individuals can file complaints if their data is mishandled.
- Right to Nominate — Individuals (principals) can nominate another person to exercise rights in the event of death or incapacity.
- Duty for Legitimate Grievance Redressal — Data principals must not register a false or frivolous complaint.
- Duty for Data Accuracy — Data principals must not furnish any false particulars or impersonate another person in specified cases.
The duties of Data Principals under the DPDP Act are:
- To comply with the legislation.
- Not to impersonate another person.
- Not to suppress any material information.
- Furnish only such information as is verifiably authentic.
Violation of duties will be punishable with a penalty of up to ₹10,000. Obligations of Data Fiduciaries and Data Processors Entities handling personal data (data fiduciaries) and individuals handling personal data on behalf of such entities (data processors) must:
- Ensure lawful data processing with consent and legitimate use.
- Protect data against data breaches by taking reasonable security safeguards.
- Notify authorities (Data Protection Board of India) and affected individuals in case of data breaches.
- Store data only in locations that are not blacklisted / prohibited under the Act.
- Ensure compliance with data retention and deletion policies.
- Make reasonable efforts to ensure the accuracy and completeness of data.
Data Protection Board of India The Data Protection Board (DPB) is the regulatory authority responsible for enforcing the DPDP Act. It has the power to investigate data breaches, impose penalties and handle grievances from individuals.
DPDP Act penalties The DPDP Act, 2023 introduces strict penalties for noncompliance. Organizations that fail to adhere to data protection requirements may face significant financial consequences.
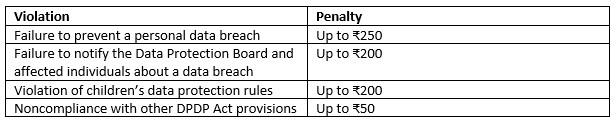
Implications for businesses
- Hefty fines — Organizations handling large volumes of personal data must implement robust security measures to avoid penalties.
- Reputational damage — Data breaches and noncompliance can lead to loss of customer trust and business credibility.
- Regulatory scrutiny — The Data Protection Board of India has the authority to investigate and enforce compliance, increasing oversight on businesses handling personal data. With these penalties in place, businesses must take proactive security measures to ensure compliance, prevent breaches and avoid financial and reputational risks.
Exemptions from the DPDP Act
Certain organizations and scenarios may be exempt from specific provisions of the DPDP Act, including:
- Government agencies for national security or law enforcement purposes.
- Certain small businesses based on processing volume and nature, e.g., personal data processed for any personal or domestic purpose and personal data that is made publicly available by the Data Principal to whom such personal data relates.
- Data processing for journalistic, research or archival purposes.
What the DPDP Act means for managed service providers (MSPs)
Managed service providers (MSPs) play a crucial role in securing and managing IT environments for businesses of all sizes. The DPDP Act, 2023 introduces new responsibilities for MSPs handling personal data on behalf of their clients.
Key implications for MSPs
1. Increased compliance burden — MSPs must ensure their services align with DPDP Act requirements, including secure data handling, breach notification and compliance reporting.
2. Data storage and localization — MSPs serving Indian clients need to ensure personal data is not stored in restricted countries.
3. Incident response and breach management — Since MSPs often manage cybersecurity for their clients, they must have robust mechanisms for detecting, reporting and mitigating data breaches.
4. Data retention and deletion policies — MSPs must implement clear policies for data retention and deletion, ensuring compliance with client requirements and regulatory mandates.
5. Security as a service — With growing compliance demands, MSPs have an opportunity to offer managed security services, including data loss prevention (DLP), endpoint detection and response (EDR) and compliance monitoring.
How MSPs can stay compliant
To maintain compliance and enhance security, MSPs should:
- Implement advanced cybersecurity solutions such EDR, XDR and DLP to protect personal data.
- Ensure data storage practices align with DPDP Act regulations.
- Use automated tools for breach detection and reporting.
- Offer cyber resilience services, including data backup, recovery and risk assessment.
With these strategies, MSPs cannot only comply with the DPDP Act, but also position themselves as trusted partners in the data protection and security space.
How Acronis can help you comply with the DPDP Act
Acronis provides a portfolio of natively integrated cybersecurity, data protection and management solutions, designed for MSPs (and by extension, businesses they serve) to help organizations meet key DPDP Act requirements. Here’s how:
1. Protecting personal data
Solution: Acronis EDR and XDR and Acronis Advanced Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
- How it helps:
The award-winning and AI-guided Acronis EDR and XDR safeguard against cyberthreats like ransomware and advanced attacks, ensuring sensitive information remains protected, whether on the endpoint (workstation or server) or in emails, cloud apps, a network or when related to identity. Furthermore, with Acronis EDR and XDR, partners and organizations can ensure that business continuity remains uninterrupted by rolling back attack changes, or recovering as part of incident response.
Acronis DLP prevents unauthorized access and data exfiltration — with the fastest time to value in the market. Automatically create and fine-tune DLP policies per organization by observing user behavior.
2. Ensuring data authenticity
Solution: Acronis Advanced Backup with ML-based data validation
- How it helps: Ensures stored data remains untampered and authentic. Acronis’ machine learning-powered validation detects corruption or unauthorized changes in backup files, maintaining data integrity.
3. Informing the Data Protection Board and affected individuals in case of a breach
Solution: Acronis EDR and XDR
- How it helps: Automatically monitors and correlates events to provide real-time visibility into a prioritized list of security incidents — helping you focus on what’s most important. At the same time, our solution streamlines incident analysis with unparalleled AI-guided summaries and attack interpretations, empowering lower tier technicians to analyze with ease and speed. Last, but by no means least, it provides automated reporting capabilities, enabling quick compliance with the DPDP Act’s breach notification requirements.
4. Ensuring data is not stored in restricted countries
Solution: Acronis global and India-based data centers
- How it helps: Acronis operates India-based data centers, ensuring organizations have a way to store personal data locally. While the DPDP Act doesn’t explicitly prohibit cross-border data transfers, it operates a list of blacklisted countries, and Acronis’ 53 other data centers worldwide can help ensure sovereignty and compliance across the globe.
5. Data retention and deletion compliance
Solution: Acronis Backup and Recovery
- How it helps: Enables businesses to set automated retention policies and ensure timely deletion of personal data, helping meet legal and compliance obligations.
6. Continuous monitoring and risk assessment
Solution: Acronis RMM
- How it helps: Provides real-time, AI-based monitoring of IT systems, detects and mitigates vulnerabilities, streamlines processes via scripting and ensures proactive risk management to prevent potential compliance violations.
Conclusion and next steps
The DPDP Act, 2023 marks a significant step toward stronger data protection in India. Compliance is essential; not just for legal reasons, but also for maintaining client trust and securing sensitive information. Acronis’ natively integrated cybersecurity, data protection and management solutions provide MSP partners and businesses with the tools they need to align with key regulatory requirements — ensuring security, compliance and peace of mind. If you’re looking to enhance your data protection strategy and comply with the DPDP Act, Acronis has got your back.
About Acronis
A Swiss company founded in Singapore in 2003, Acronis has 15 offices worldwide and employees in 50+ countries. Acronis Cyber Protect Cloud is available in 26 languages in 150 countries and is used by over 21,000 service providers to protect over 750,000 businesses.



