If you run a business and don’t think your organization is a target for cyberattacks, we invite you to read on and discover just how safe you are!
What is a Cyber Attack?
A cyberattack is typically any online incident initiated by a cybercriminal or cybergang that attempts to steal data or money, encrypt data, use an infected system to launch more attacks, or otherwise harm a user’s computer or business’s IT environment. Some examples of cyberattacks include malicious spam, malware attacks, ransomware, phishing attacks, business email compromise (BEC) attacks, denial of service (DDoS) attacks, SQL injection, social engineering attacks, and zero-day exploits.
Why do cyberattacks happen?
Cybercriminals attack nation states, government agencies, and businesses for a variety of reasons. While financial gain is the most likely reason for an attack, attackers also have other objectives.

Financial gain – Many cybercriminals are in business to make money by stealing a business’ confidential information, personally identifiable information (PII), or other sensitive data (e.g., credit card information). Once the attacker has stolen this data, they can hold the data “ransom,” commit identity theft, steal money from financial accounts, dupe a business or individual into transferring money into fraudulent accounts, or do something that makes them vulnerable to further attacks. In 2020, 63% of cyberattacks were financially motivated.
Revenge – Disgruntled and terminated employees launch attacks to create chaos and disrupt a business’s operations to exact revenge for what they consider to be unfair actions against them. The intent is to damage the organization’s reputation and brand. An attack perpetrated by an individual with inside knowledge of an organization’s systems and procedures is an insider attack. Insider attacks can sometimes be non-malicious, e.g., an employee accidentally deletes critical data or downloads cracked software to accomplish a business function, but that software includes a virus.
Nation states also launch cyberattacks to “advance their national interests, intelligence gathering capabilities, and military strength through espionage, disruption and theft.” According to one study, there has been a 100% rise in ‘significant’ nation state incidents between 2017-2020.
Cyberwarfare – Any cyberattack that has the objective of disrupting a nation state’s IT infrastructure for political, religious, social, or economic reasons is considered cyberwarfare. Studies show that 26.3% of all cyber warfare strikes are directed towards the United States, and that as many as 35% of all politically-motivated cyberattacks have links with China or Russia.
Competitive advantage – Competition drives cyberattacks and in recent years, DDoS attacks have been used to attack the website of a competitor and overwhelm the website’s capacity to handle multiple requests and bring the site down. The ultimate objective is to drive customers to the “attacking” business. Other common attacks focus on websites directly. These include malicious redirects, spam injections, and “hacked by” pages that replace a website’s index page with a page generated by the attacker. These attacks are intended to create a lack of confidence in the victim, thereby driving traffic to their competitors.

Why are SMBs the most attractive targets for cybercriminals?
Even though many small-to-medium-sized business (SMBs) executives believe their companies are “too small to target,” SMBs are one of the most attractive targets for a cyberattack. Attackers know that SMBs are “in denial” when it comes to cyberthreats and do not take the appropriate actions to safeguard and secure their systems and data. This alone makes SMBs a prime target for an attack.
Lack of a cyber security infrastructure – Many SMBs are still running legacy software, which does not provide the security features to thwart modern-day attacks. In some cases, the software is at end of life, so no updates are available. In other cases, the business may not install software patches on a timely basis. Both scenarios introduce security gaps and make it easy for cybercriminals to gain entrance to the business’s network and end points.
Lack of IT professionals / IT department in the company – Limited budgets not only mean that an SMB cannot afford to purchase sophisticated cyber security software, but it also means they cannot afford to hire many (if any) IT experts. If a business hires in-house IT expertise, these one or two individuals are IT generalists charged with maintaining servers, PCs, applications, databases, and so on. Hiring a cyber security analyst is expensive, especially considering the shortage of talent.
Lack of user training – Limited budgets also mean that an SMB cannot afford and/or take the time to train users on what cyberattacks look like, and what to do, or what not to do. Busy employees who suffer from email fatigue tend to make quick – and usually bad – decisions, such as clicking on a link or visiting a strange website without thinking. In fact, a recent study revealed that 95% of cyber security breaches are caused by human error.
Weak passwords – Many attackers target SMBs knowing that untrained employees tend to use weak passwords. Weak passwords are responsible for 81% of hacking-related data breaches. Despite this statistic, many users still do not recognize the importance of strong and unique passwords. According to a separate study, 59% of people reuse passwords across multiple, if not all, sites.
Best cyber security practices to avoid attacks
Here are five best practices every business should follow to thwart cyberattacks.
Educate employees to spot signs of attacks – It is important that every business provide their users with continuous cyber security training. Users need to know what kinds of attacks they can expect, what they look like, what to do, and what not to do.
Implement multi-factor identification – Multi-factor authentication is a feature that requires a user to present at least two different types of identity evidence before being allowed to access an account. This includes something the user knows and something they have access to. Multi-factor authentication provides a second layer of protection for a user’s accounts – above and beyond the user’s password. 2FA is the most highly recommended defense to block an attacker from hijacking a user’s account.
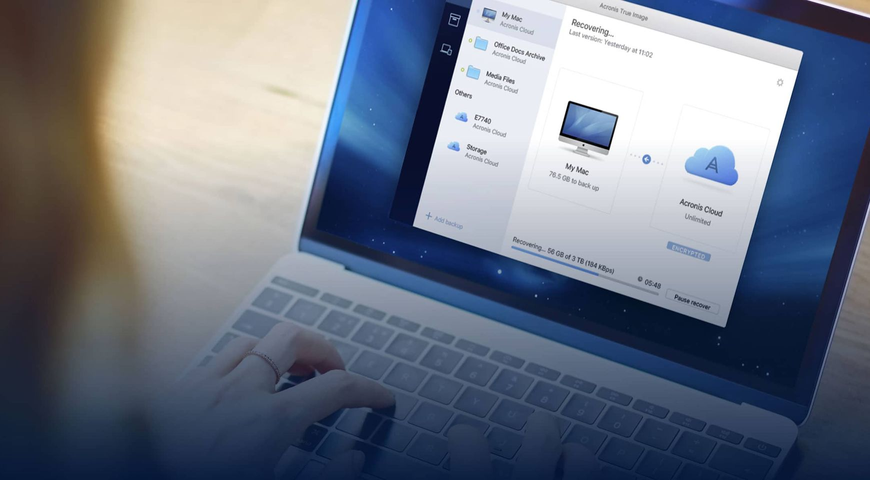
Implement a backup strategy – Every business, regardless of size, must back up their systems and data. Like death and taxes, data loss is inevitable, and no cyber security solution is 100% effective 100% of the time. Businesses and managed service providers should always follow the 3-2-1 backup rule: keep your data in three places (a production copy and two backups), across two media, with one backup stored offsite, such as in the cloud.
Develop a disaster recovery strategy – Disaster recovery refers to how companies recover their systems and data after a human-made or natural disaster. Disaster recovery relies upon replicated production data that is backed up to an offsite location, be it a different data center, office, or in a private or public cloud. When a disaster strikes, the organization can recover its data from these backups. In some cases, the organization will use the offsite location as its production site until the original site is back up and running. Any business that collects data needs to have a secure and well-structured disaster recovery strategy. Failure to do so not only results in massive data loss, but can also seriously damage a business’s credibility and reputation in the market. Businesses without a disaster recovery strategy put themselves at serious risk of going out of business.
Invest in cyber protection software – While cyber security software can protect your business from a breach, it does not fully protect your systems, applications, and data. Alternatively, cyber protection is an integrated solution that combines cyber security, backup, and disaster recovery, ensuring your systems, apps, and data are secure and protected, no matter what happens – a malicious attack, deleted data resulting from human error, corrupted data due to hardware/software malfunctions, a human-made or natural disaster. In essence, any event that causes data loss.
Acronis Cyber Protection solution for businesses
Acronis offers businesses an cyber protection solution that natively integrates cyber security, data protection, and management to protect endpoints, systems, and data.
Acronis Cyber Protect (includes Acronis Cyber Backup) provides SMBs with:
- Business cyber security and endpoint protection management, vulnerability assessments and patch management, remote desktop, and drive health
- Full-stack, next-generation machine intelligence (MI)-based protection against malware, including URL filtering and automated backup scanning
- Fast and reliable recovery of your apps, systems, and data on any device, from any incident
Acronis Cyber Protect (includes Acronis Cyber Backup) utilizes a revolutionary approach to cyber protection. By integrating data protection with cyber security, these solutions eliminate complexity, deliver better protection against today’s threats, and maximize efficiency by saving time and money.
About Acronis
A Swiss company founded in Singapore in 2003, Acronis has 15 offices worldwide and employees in 50+ countries. Acronis Cyber Protect Cloud is available in 26 languages in 150 countries and is used by over 20,000 service providers to protect over 750,000 businesses.