Cyberthreats are more prevalent than ever and one of the most effective cyber exploits preys on outdated software, both operating systems (OSs) and applications. Cybercriminals focus on popular OSs and applications, such as Windows, Java, Adobe, and Microsoft 365, looking for vulnerabilities to exploit. This is why a patch management system is imperative.
What is a patch management system?
All reputable software providers release IT and security patches on an ongoing basis to add improved functionality, enhance performance, and close security loopholes and vulnerabilities in their OSs or applications. Patch management centralizes and automates the detection, acquisition, installation, and reporting of these patches on your systems, eliminating the workhours IT spends manually looking for and applying patches on servers and desktops across the organization.
Patch management systems can be a separate product, or a part of a larger cybersecurity suite. The product/feature manages multiple software patches, keeping your infrastructure up-to-date and protected from threats. In organizations, patch management is typically controlled by a system administrator who configures the software according to the organization’s security policy, structure, and needs, including specific functionality requirements. Patch management ensures that patches are applied on a timely basis and are not subject to time delays because the patch is overlooked, or IT resources are stretched.
When patching software isn’t automated, IT and business users are not as careful about performing regular updates, which is why software developers are continuously improving and automating update procedures for their products. Without reporting on patch management, you cannot be sure that the software was correctly installed or if any software patches failed.
IT patches address vulnerability gaps
Vulnerability patching is an important part of a proactive, multilayered cyber protection strategy. If IT patches are not installed on a timely basis, your organization can – and probably will – be a victim.
The Equifax data breach, one of the biggest known data thefts to date, is an example of what happens when patching is not timely. A critical vulnerability in the Apache Struts software was disclosed on March 7, 2017. Despite being alerted by the Department of Homeland Security on March 8, “Equifax did not fully patch its systems … leaving its systems and data exposed. On May 13, 2017, attackers began a cyberattack on Equifax which lasted for 76 days…”
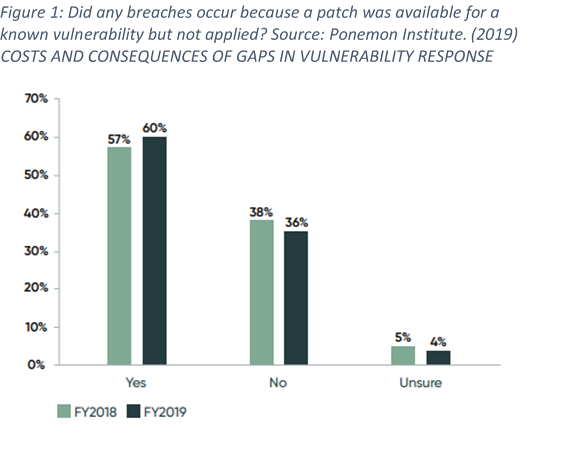
Regardless of the cyberattacks we read about in the news, many organizations are still not regular with patch management and patch monitoring. A Ponemon Institute survey discovered that:
- 60% of breach victims said they were breached due to an unpatched known vulnerability where the patch update was not applied. (see Figure 1).
- 62% were unaware that their organizations were vulnerable prior to the data breach.
- 52% of respondents said their organizations are at a disadvantage in responding to vulnerabilities because they use manual processes.
Manual vs automated patch management: advantages and disadvantages
There are few good reasons why you would manually install and manage patches. While it can work well for small organizations with only a few devices to manage, it does not bode well for medium-sized and larger organizations.
Manual patching takes too much time and is prone to admin error than an automated process. When patching isn’t transparent and automated, IT admins are not nearly as careful about performing them regularly. Manual software patch errors can occur for various reasons. An IT admin can inadvertently skip patching a system, may have a missed a failed update notification or accidently pushed a wrong version of the software update. With automated patching and reporting, these problems will not happen.
It is no wonder that a recent survey discovered that 71% of IT and security professionals found patching to be overly complex, cumbersome, and time consuming and 57% of respondents stated that remote work has increased the complexity and scale of patch management.
How to sell patch management to your clients as an MSP
All businesses, regardless of their size, understand that patch management is important. The reason patching is not timely is usually due to internal IT staff shortages and/or prioritization problems. This is the reason why many organizations should use an MSP to handle patch management.
Patch management systems ensure:
Security. Timely patch management safeguards your clients’ data, applications, and systems. Critical patches must be applied as soon as possible to avoid data theft and severe brand damage that often follows a security breach.
Compliance with regulatory requirements. Timely patch management minimizes data leaks and adds to your clients’ data protection. This is especially important for government institutions, healthcare organizations, and organizations in the financial sectors who can face huge losses – due to the compliance penalties alone – following a data leak resulting from an unpatched vulnerability.
Continued user productivity. If a machine is hacked and rendered useless because of an unpatched vulnerability or after a bad patch is applied, the client’s users can be impacted.
Business continuity. A breach can be so severe that it can bring down your systems and stop business operations.
Improved system performance. Patching your OS and applications ensures that you have the latest and greatest features the vendor has to offer, and it can also improve system performance.
A good patch management solution addresses all these challenges.
The MSP patch management process
These are the key steps every MSP should follow to support the patch management process. Many cybersecurity providers, like Acronis, provide patch management, vulnerability assessment software, tools to assist with developing a software/hardware inventory, and the ability to backup your client’s systems and scan the backups to be sure they are not infected.
Inventory and standardize your client’s systems. This exercise should be performed on a monthly or quarterly basis, and it should include information on hardware and software, including the operating systems/versions, applications/versions, IP addresses, physical location and asset owners. As part of this step, you should collaborate with your client to standardize their OSs and applications to the same version. This will make patching faster and easier going forward.
Identify what patches are available. While it is easier to identify patches for your operating systems, you may need to do further research to identify what patches are available for third-party software that your client is using.
Identify all technical security controls. This includes any hardware or software used to protect your client’s assets, including authentication solutions, firewalls, antivirus software, VPN, encryption measures and so on.
Perform a vulnerability assessment and prioritize patching. A vulnerability assessment (VA) is a process of identifying, quantifying, and prioritizing found vulnerabilities in the system. Once completed, compare the vulnerabilities against your asset inventory to identify which patches to prioritize.
Test. This is a critical step as you want to apply patches to a sample of assets and evaluate the machines to ensure the patches were successfully installed and do not cause any issues.
Apply the patches. Once testing is complete and successful, start to apply patches to those assets that are at the highest risk and need immediate remediation. Modern patch management systems will let you:
- Install OS-level and application-level updates
- Approve patches manually or automatically
- Install patches on-demand or according to a schedule
- Precisely define which patches to install by different criteria: severity, category, and approval status
- Perform pre-update backup to prevent possible unsuccessful updates
- Define the reboot action after patch installation
Confirm successful patching. Be sure that each patch was applied successfully.
Acronis Cyber Protect Cloud: Vulnerability assessment and patch management capabilities
As a cyber protection company, Acronis covers all aspects of cybersecurity to provide seamless business continuity for its partners and customers. Vulnerability assessment and patch management capabilities are important parts of Acronis’ cyber protection proposition, which centralizes your security posture in one management console and one agent, eliminating typical security management complexity.
Acronis Cyber Protect Cloud's vulnerability assessment and patch management functions provide detailed information about devices and applications running on your network. Vulnerabilities are classified according to an internal severity scale and required updates are automatically fetched and rolled out to different groups in a variety of ways by tweaking the corresponding protection plan.
Acronis distributes patches from its cloud servers around the world and uses a peer-to-peer patch distribution technology to prevent slowdowns during patch rollout for non-Windows systems and third-party applications. Updates, upgrades, and applications can contain packages with exceptionally large files. Downloading and distributing these large files can consume network resources on the devices receiving them. Acronis uses delivery optimization to reduce bandwidth consumption by sharing the work of downloading these packages among multiple devices in a customer’s deployment.
Acronis Cyber Protect Cloud supports Windows-based and Linux networks. The solution patches endpoints, whether they are located inside or outside the corporate network.
The patch management functionality can also be used in unique safe restore scenarios from a full-disk backup. The safe restore feature guarantees you are protected by updating anti-malware bases of the Acronis Cyber Protect Cloud agent in this full-disk backup to the latest definitions and Artificial Intelligence (AI) models. This allows you to detect malware and prevent it from attacking already patched systems.
About Acronis
A Swiss company founded in Singapore in 2003, Acronis has 15 offices worldwide and employees in 50+ countries. Acronis Cyber Protect Cloud is available in 26 languages in 150 countries and is used by over 21,000 service providers to protect over 750,000 businesses.



