According to the Acronis Cyberthreats Report 2020, 31 percent of companies worldwide reported being attacked during 2020. Ransomware encryption looms as one of the most prominent and dangerous of cyberthreats and with remote working dominating the landscape in 2021, it is expected that cyber-attacks will only increase. As a comparison, our experts at the Acronis Cyber Protection Operations Centers (CPOCs) discovered that more than 1,000 organizations around the world had their data leaked following a ransomware attack in 2020.
What is ransomware encryption?
Ransomware encryption is a type of malware, known as cryptoware, which encrypts the files on a user’s computer so that they cannot access the data until a ransom is paid. The attacker may threaten to permanently delete the encrypted files or publish sensitive information unless your organizations pays the ransom by a specific deadline. Ransomware encryption comes through email attachments and infected files downloaded with multimedia from malicious websites.
By the time the user identifies ransomware on their computer, it will be too late to save the data. Attackers install ransomware on any given computer, typically with a user’s unwitting help when they open an attachment or click on a link. In the background, the ransomware starts to encrypt the files and once complete, the user sees a message like the following on their screen.
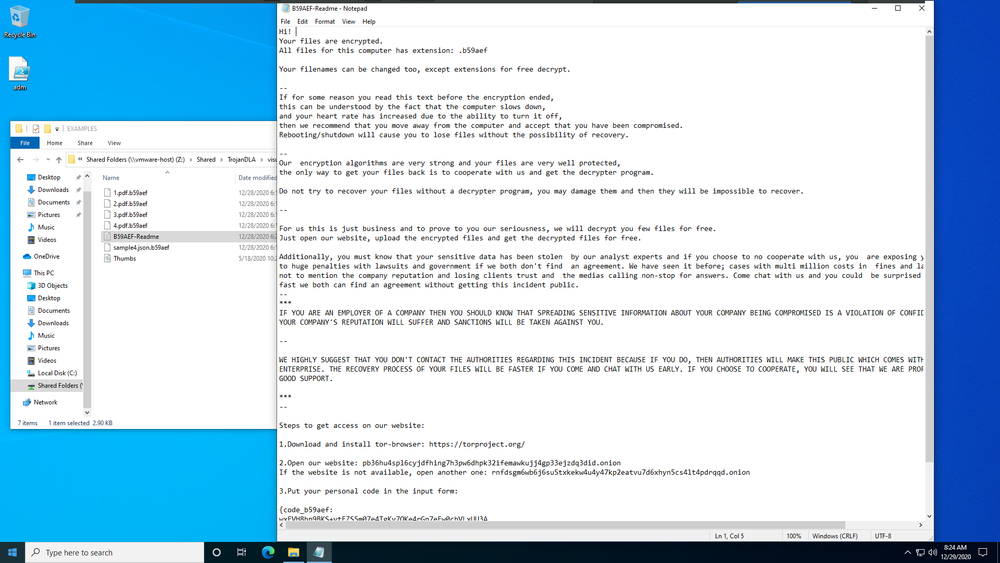
Ransomware may also attempt to spread to other systems on your organization’s network, including local backup servers.
What encryption does ransomware use?
Encryption is a security tool that is used to protect, secure, and make data private. While all organizations encrypt their files as a defensive security measure, attackers use encryption as part of their ransomware strategy.
A ransomware infection that encrypts data uses cryptography and malware to infect a computer and encrypt the data residing there. Cryptography uses military-grade algorithms and secret keys to encrypt and decrypt data.
Ransomware decrypt methods
While there are ransomware decrypt tools available to help you decrypt files (and some of these tools are available at no charge), you may discover these tools may not work in time or not work at all, especially if the ransomware is a new variant or is frequently updated. The bottom line is that it is almost impossible to decrypt the data without a private key. It has been known to happen but do not “bet the bank” on it.
How to remove ransomware encryption?
If your organization is a victim of a ransomware encryption attack, you have a limited number of options available to get the data back:
- Restore the infected system from a cloud or off-line backup. If you have on-site backups, chances are that this data may also be encrypted or deleted by the attacker.
- Use ransomware decrypt tools or hire a ransomware recovery expert who specializes in ransomware decryption. This option can be risky business – as we mentioned previously – and may not work in time or not work at all.
- Format the infected computer’s hard drive and re-install the operating system and applications. Unfortunately, with this option, all data will be lost, making this a less desirable option.
- Pay the ransom and pray that the data will be restored. Be aware that with this option, there are no guarantees that the attacker will deliver the decryption key.
How to protect your organization from ransomware?
To protect your organization’s computers from ransomware, you need to:
- Back up everything that is on each computer to the cloud, including the operating system, applications, and data. In fact, be sure to follow the 3-2-1 backup rule, which stipulates that you have:
- Three copies of your data, one production version and two backups
- Two formats for your backup, network drive, external hard drive, cloud, etc.
- One of those backups must be stored off-site, like in the cloud.
- Purchase a cyber security product that can detect and stop ransomware before it cripples any employee’s computer and hijacks their data.
While some products that are sold as anti-ransomware can stop attacks, they do not help you recover from the damage that occurred prior to detecting the attack. Other products can assist in post-attack recovery, but only recovery of smaller files.
The fact is: traditional security tools, which are a conglomeration of tools for backup, patch automation, antimalware, configuration management, etc. are not designed to handle modern cyberthreats.
As a result, Acronis has modernized the 3-2-1 backup rule. To achieve the same level of protection the 3-2-1 rule originally delivered, it is important to incorporate cyber security capabilities with data protection best practices.
Acronis Cyber Protect: Made for modern ransomware threats
Acronis Cyber Protect is different than any other cyber security solution. In fact, it is the only solution that natively integrates cybersecurity, data protection, and management to protect endpoints, systems, and data. The solution provides:
- Proactive protection: Includes vulnerability assessments and patch management, removal of malware from backups, managing computer health
- Active protection: Includes continuous data protection, real-time malware defenses, self-defense capabilities
- Reactive protection: Provides integrated disaster recovery, forensic backups, ability to co-exist with other security solutions
In addition to enabling flexible backup and recovery storage options that adhere to the 3-2-1 rule of backup, Acronis Cyber Protect offers built-in AI-based anti-ransomware technologies designed to detect and prevent ransomware attacks from costing your organization time and money. Plus, the solution enables easy vulnerability assessments to identify vulnerabilities and prevent cybercriminals trying to exploit operating system or application security gaps.
Acronis Cyber Protect detects and terminates ransomware attacks, then quickly and automatically restores any damaged files regardless of their size. Acronis Cyber Protect offers one agent, one management interface, and one license – removing the complexity and risks associated with non-integrated solutions, minimizing ransomware incidents, and increasing productivity.
For more information about global cybersecurity trends and predictions for 2021, you can read Acronis Cyberthreats Report 2020.
About Acronis
A Swiss company founded in Singapore in 2003, Acronis has 15 offices worldwide and employees in 50+ countries. Acronis Cyber Protect Cloud is available in 26 languages in 150 countries and is used by over 21,000 service providers to protect over 750,000 businesses.



